Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a set of practices, processes, and tools used to manage the entire life cycle of an application, from conception to retirement.
Top 7 Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Software & Tools List
ORCANOS

Orcanos integrates ALM (Design control), Quality Management, and Regulatory Compliance into a single SaaS platform, providing a comprehensive solution for companies in the medical device industry.
- Single Repository for R&D Quality And Regulations
- End-To-End Traceability
- DHF Document Generation
- Impact Analysis
- Just Start Working…
SAP
SAP provides digital support experience with solutions for autonomous Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) and service and support delivery for all customers and landscapes, integrating the products that make up the Intelligent Enterprise.
- Collect business demand regarding new or changed business processes
- Convert requirements into detailed specifications
- Configure the applications and check if they match the requirements
- Transfer changes from a test environment into the live business
- Provide services required for ongoing operations
- Analyze service-level fulfillment and perform any activities required to improve results
PDSVISION
Pdsvision – manage your software data PTC Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) which now is a part of PTC Windchill the Product Lifecycle Management (PLM).
- Software change and configuration management
- Integration with source code tools like GIT, Subversion, JIRA etc.
- Requirements definition and management – including agile automation
- Change, issue and defect tracking
- Testing
- Reporting and metrics to support business intelligence
- Verification and Validation
PERFORCE

Helix ALM delivers continuous traceability for complex development. Requirements management, test case management, and issue tracking – all in one place.
- Requirements Management
- Testing Management
- Issue Tracking
- Traceability Matrix
- Automated Workflows
- Risk Management
- Metrics & Reports
- Integrations
KOVAIR
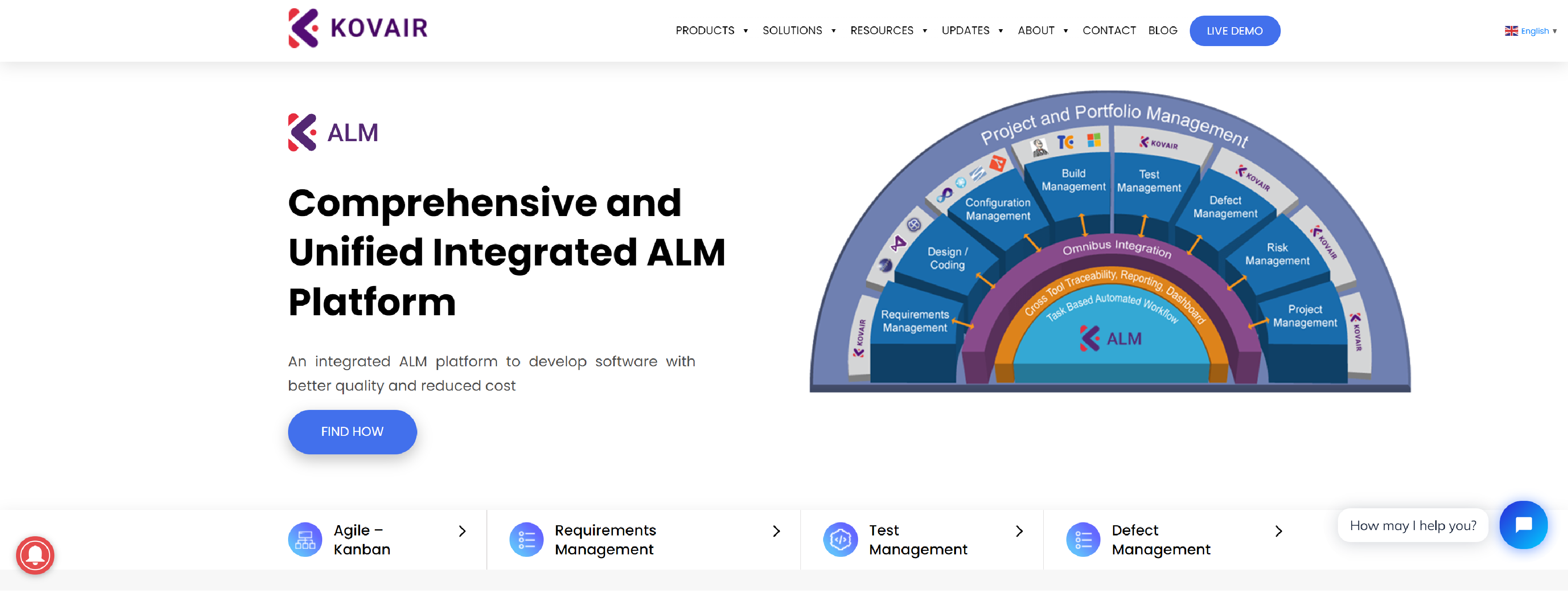
Kovair ALM provides end-to-end Application Lifecycle Management – ALM solutions – Requirements, Test, Issues, Project, Risk, and Release Management.
- Comprehensive Integrated ALM
- Unified platform
- Better governance
- Tailor as per your need
- Manage complex projects
- Complete visibility
ROCKETSOFTWARE
Rocket Software provides IT modernization and IT automation solutions that help businesses solve their most complex IT challenges, across infrastructure, data, and applications.
- Software change management that makes it easy to embrace change
- IT workflow automation brings speed to your processes
- Rocket DevOps release management takes the fear out of managing releases
- Rocket DevOps deployment management
- IT compliance is a piece of cake with our ALM software
ROMMANASOFTWARE
Rommana Software has the most complete Application Lifecycle Management tools that was recognized as one of the Best ALM Tools. Find out more abot what ALM software should provide.
- Full Integration and traceability between all project artifacts and activities
- Full collaboration between all team members throughout all project activities
- Accessibility of all project artifacts and activities by all team members anywhere 24/7
- Strong methodologies with checks and balances that guide team members to follow best practices throughout all lifecycle phases
- A project management framework that is driven by features being delivered
- Total agility and flexibility to respond to continuously changing business needs and systems behaviour