Patch management software is a tool or system designed to help organizations manage and automate the process of applying patches (updates or fixes) to software applications, operating systems, and other IT infrastructure components. The goal of patch management is to ensure that systems are up to date, secure, and functioning properly by addressing known vulnerabilities, bugs, or performance issues.
Discover the top 18 patch management software solutions
Easy2patch Third-Party Patch Management
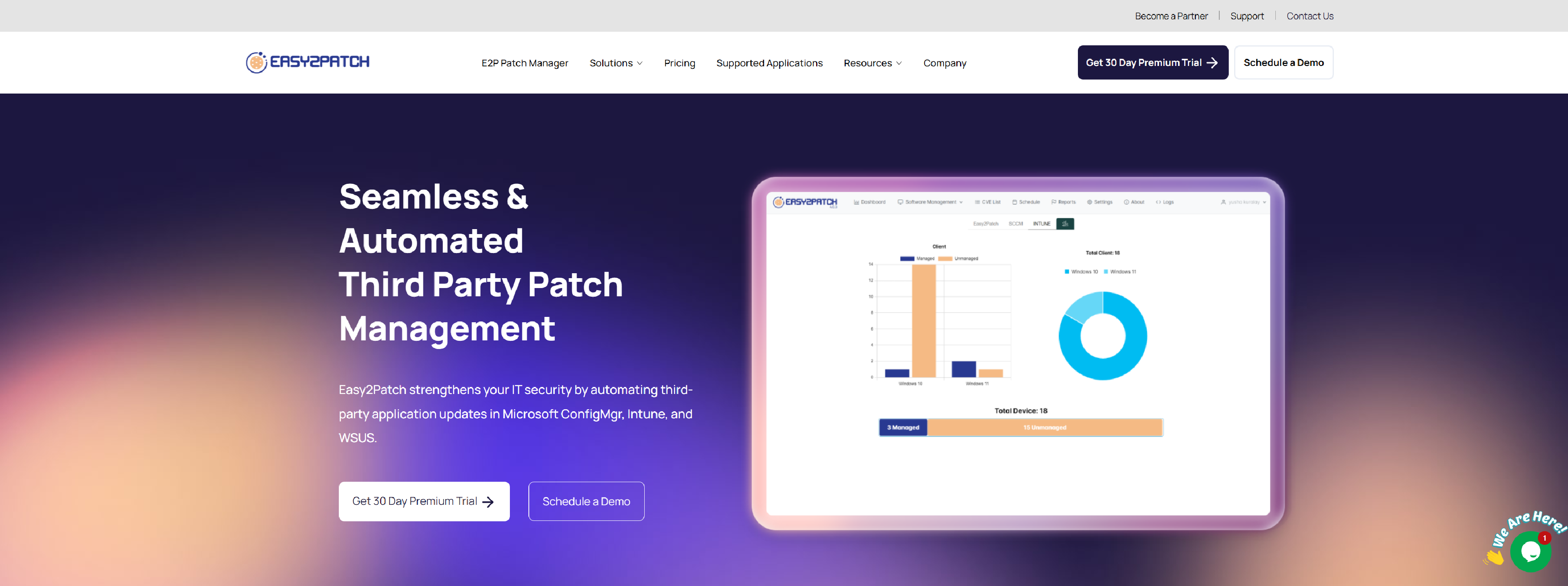
Easy2patch third-party patch management tool streamlines the patching process for effortless updates.
- Automate and centralize the update process for a wide array of applications
- Centrally manage the distribution of third-party application updates via SCCM, WSUS, and Intune
- Ensure the deployment of third-party patches to maintain system security and functionality
- Ensure patch reliability by using hash checks to verify file integrity and security
- Protect your organization’s adherence to patch management standards and regulations
- Disseminate and patch software updates across diverse devices and locations
- Deploy software updates securely without separate agents on target devices
- Customize software update deployment based on specific devices or user groups
Ivanti patch management to your Endpoint Manager

Ivanti – Patch for Endpoint Manager can swiftly detect vulnerabilities in Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and hundreds of third-party apps (Acrobat Flash/Reader, Java, Web browsers, and more) and deploy expertly pre-tested patches everywhere you need them.
- Establish and automate consistent policies for p
- Detect and remediate OS and third-party app vulnerabilities on various systems, to comply with laws and regulations
- Eliminate issues that slow user devices, and patch at the right time, under the right conditions, to minimize the impact on usersatching all of your assets, even those that are mobile, remote, or asleep
Ninjaone patch management for any endpoint
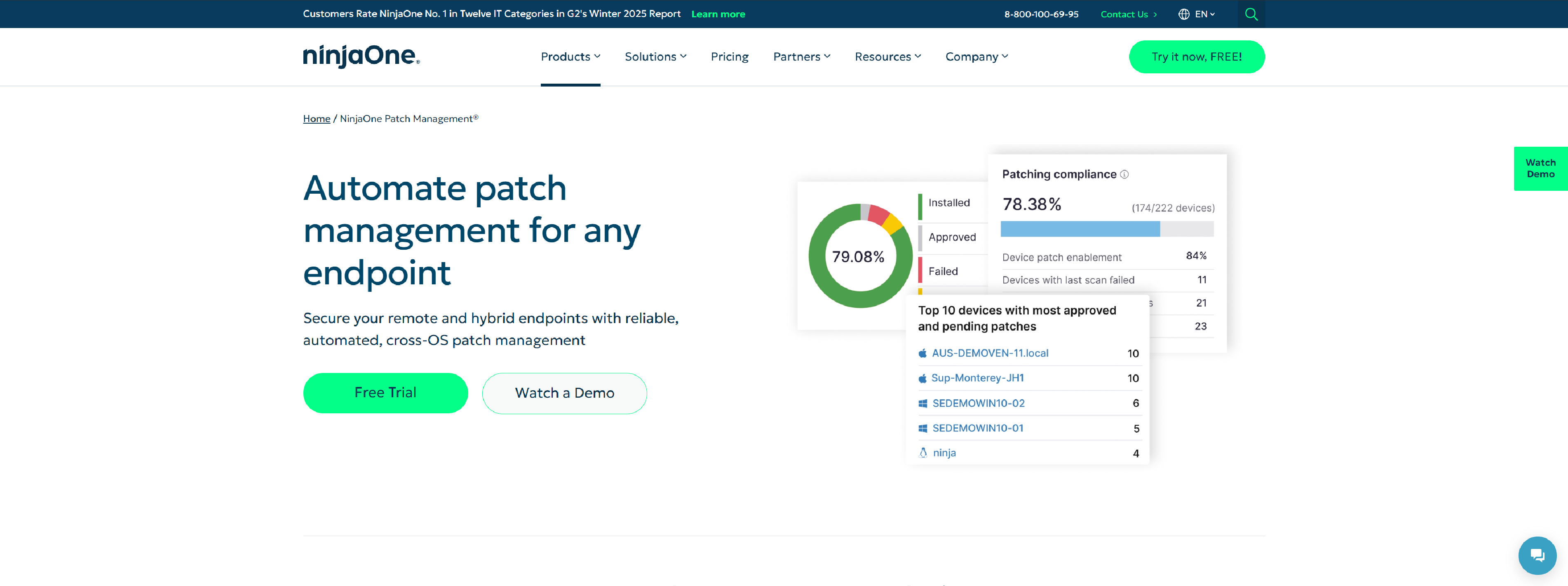
Ninjaone – Secure your remote and hybrid endpoints with reliable, automated, cross-OS patch management.
- Automatically identify, evaluate and deploy patches across Windows, Mac, Linux OSs and third-party apps
- Reduce vulnerabilities by up to 75% with automated and ad-hoc scans and granular control supported by native inclusion of CVE/CVSS
- Cloud-based, agent-deployed patching of any endpoint with an internet connection – works equally well for in-office, remote, and hybrid employees – no VPN required
Solarwinds Patch Manager
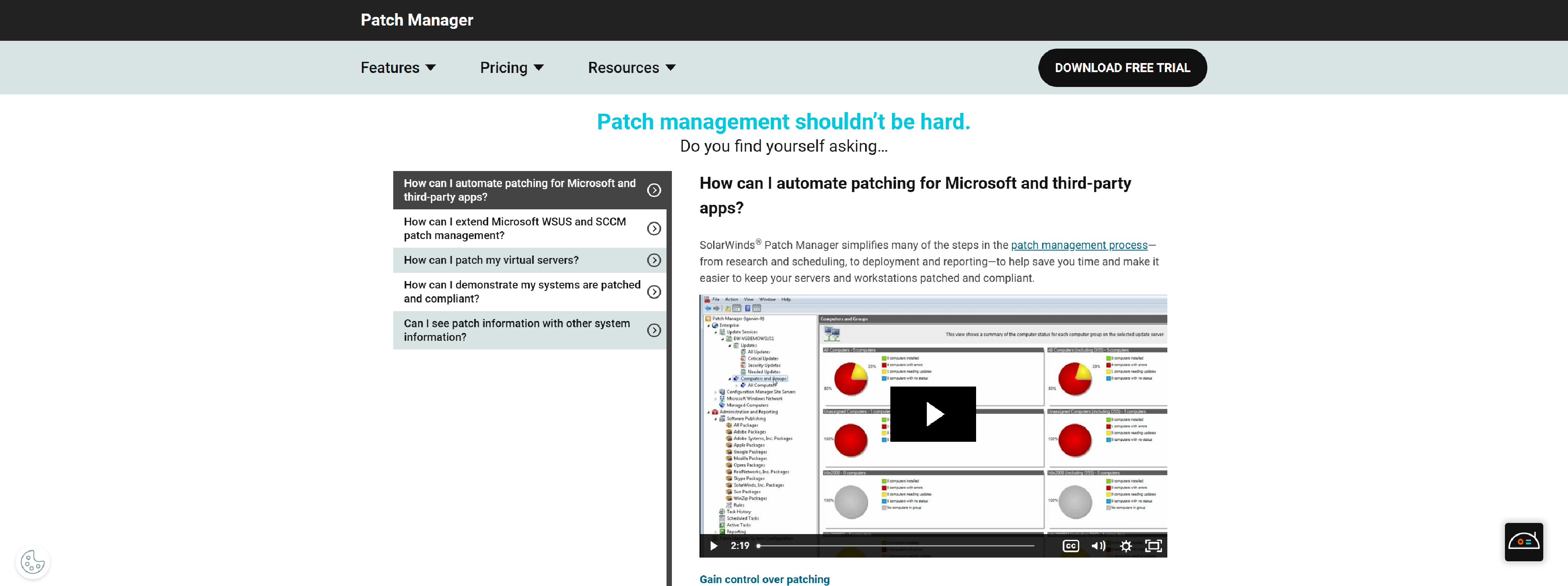
Automate patching for Microsoft servers, workstations, and third-party applications with SolarWinds Patch Manager.
- Microsoft WSUS patch management
- Integrations with SCCM
- Third-party application patching
- Prebuilt/pretested packages
- Patch compliance reports
- Patch status dashboard
Automox Patch & Endpoint Management
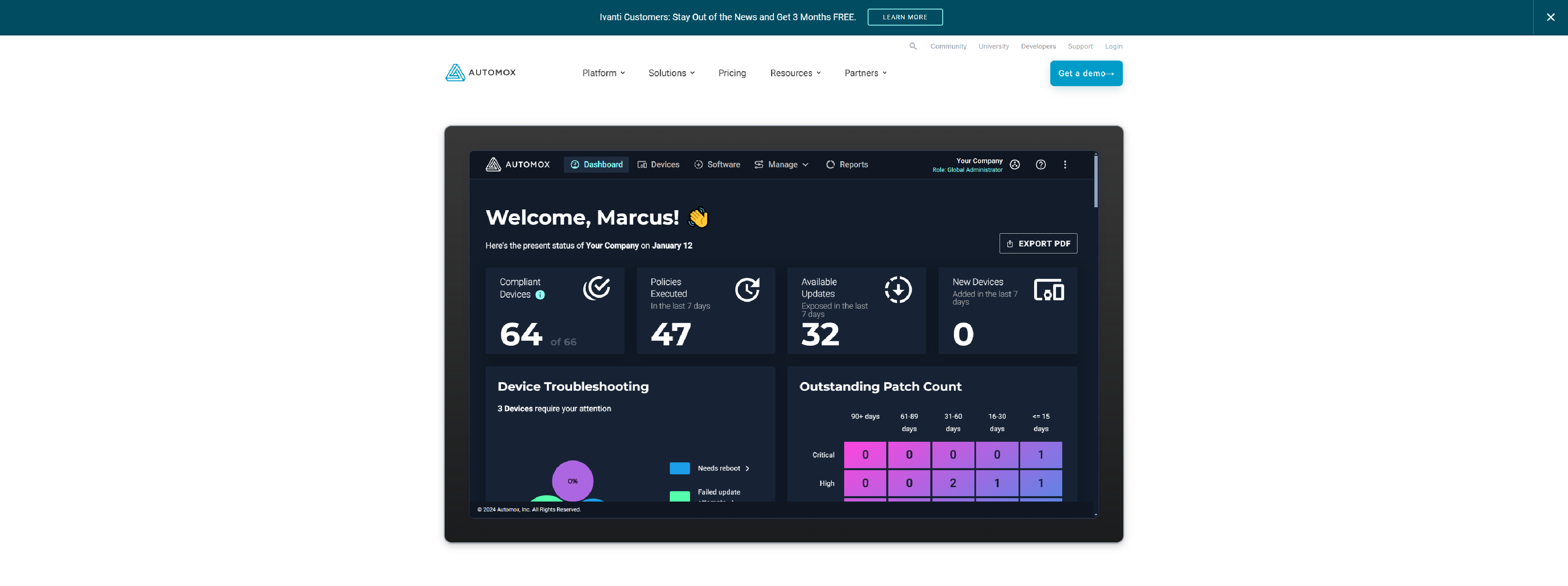
Automox’s endpoint management software automated and secures the patching, configuration, and control of all endpoints.
- Endpoint Automation from a Single Console
- Group and Tag Devices to Fit Your Needs
- Automatically Patch Third-Party Software
- Automated Patching Using Policies or Automox Worklets
Action1 Enterprise Patch Management Software
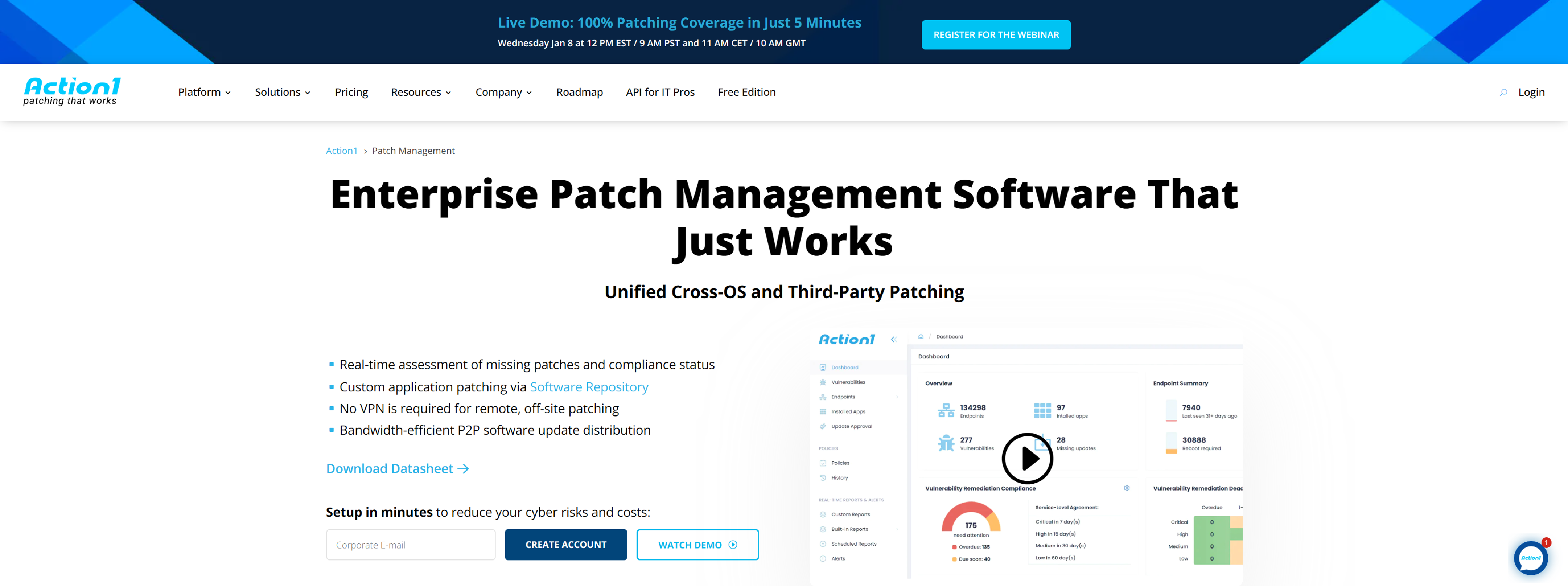
Action1 automates the patching process per patch management best practices by identifying missing updates, testing, approving, scheduling and deploying patches, as well as generating status reports.
- Install Windows Updates Remotely
- Third-Party Patching That Just Works
- Identify Missing Patches
- Patch Policy Configuration Management
- Test and Approve Patches
- Patch Management Reporting
Qualys Patch Management
Qualys Patch Management, our automated patch management solution that accelerates vulnerability remediation for all of your IT assets.
- Eliminate silos with a single platform
- Improve patch rates up to 90% with smart automation
- Stay proactive and respond faster with risk-based automation
- Fully integrated with VMDR
- Leverage zero-touch patching
- Augment your incumbent solution
Heimdalsecurity Patch & Asset Management Software for IT professionals
Heimdalsecurity – Automate patch deployment across multiple platforms, including Microsoft, Apple, Linux and third-party software.
- Bespoke, Customize or Automate – Have it your way
- Cross-platform Patching Unified – Combat tool drifting
- Over 350+ Supported Applications – Out-of-box 3rd Party Patching, Fully Automated
- Delivered in under 4 hours – Win back time and efficiency
- Policy and Compliance Management – Simplified across organization
N-able Patch Management Software for Modern IT Management
N‑able RMM, you can easily manage patching for Windows, MacOs, and third-party applications for physical, cloud servers, and endpoints.
- Design your ideal approval process to select which patches and updates go out
- Retry failed patches automatically, deploy superseding patches, and use patch rollback to spend less time fixing issues
- Deploy security patches, feature packs, Windows OS upgrades, and Out-of-band (OOB) critical updates
Goto Patch Management
GoTo Resolve patch management feature, IT teams can Identify, test, and deploy updates to applications or operating systems.
- Get more done without disrupting work. Fix problems or execute maintenance tasks, without interrupting the current user’s workflow
- Go beyond the basic requirements with technology built with a security-first mindset and zero trust architecture that locks out malicious actors
- Stay informed of potential IT management issues to keep systems up and running and identify trends before they become bigger problems
Pdq windows patch management
PDQ’s trusted history of simple, secure, and pretty damn quick Windows device patching, it’s never been easier to keep your systems running smoothly and endpoints secure.
- Improve security vulnerability management
- Reduce endpoint security vulnerabilities
- Maintain regulatory patch compliance
- Enhance software performance
- Save time for the IT security team
Kaseya Patch Management
Kaseya – Keep software patches up to date, monitor and remediate vulnerabilities and make all types of software changes from a single console.
- Keep software patching up to date to maintain security of your IT infrastructure
- Gain full control over patching including the ability to skip problematic patches by automating the process with scripts
- Easily set up patch reports to see compliance across your entire environment and quickly identify the endpoints that need attention across OS and third-party applications
- Gain visibility into vulnerabilities (CVEs) by aggregating the patch status of your IT environment in one dashboard
OpenText ZENworks Endpoint Software Patch Management
OpenText ZENworks – Automated patch management software that identifies and patches common vulnerabilities and exposures on your Windows, Linux, iOS, and Mac endpoint devices.
- Simplify your software patching process with automated tools that update your Windows devices, ensuring fast responses to security threats
- Manage patches across multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, through a single console for easier security management
- Track patch compliance on all endpoints, identify vulnerabilities, and ensure every device is up to date with automated patch deployment
ConnectWise Automate Patch Management

ConnectWise automated patch management software makes it easy to empower your IT team to patch multiple machines simultaneously.
- Streamline your IT support with hundreds of out-of-the-box scripts to monitor devices, detect problems, and automatically resolve issues
- Provide the best proactive service by monitoring for IT problems across endpoints and networks, and automate fixes without user disruption
- React fast to troubled endpoint devices with remote control; Manage multiple machines simultaneously without interrupting end users
Motadata Patch Management
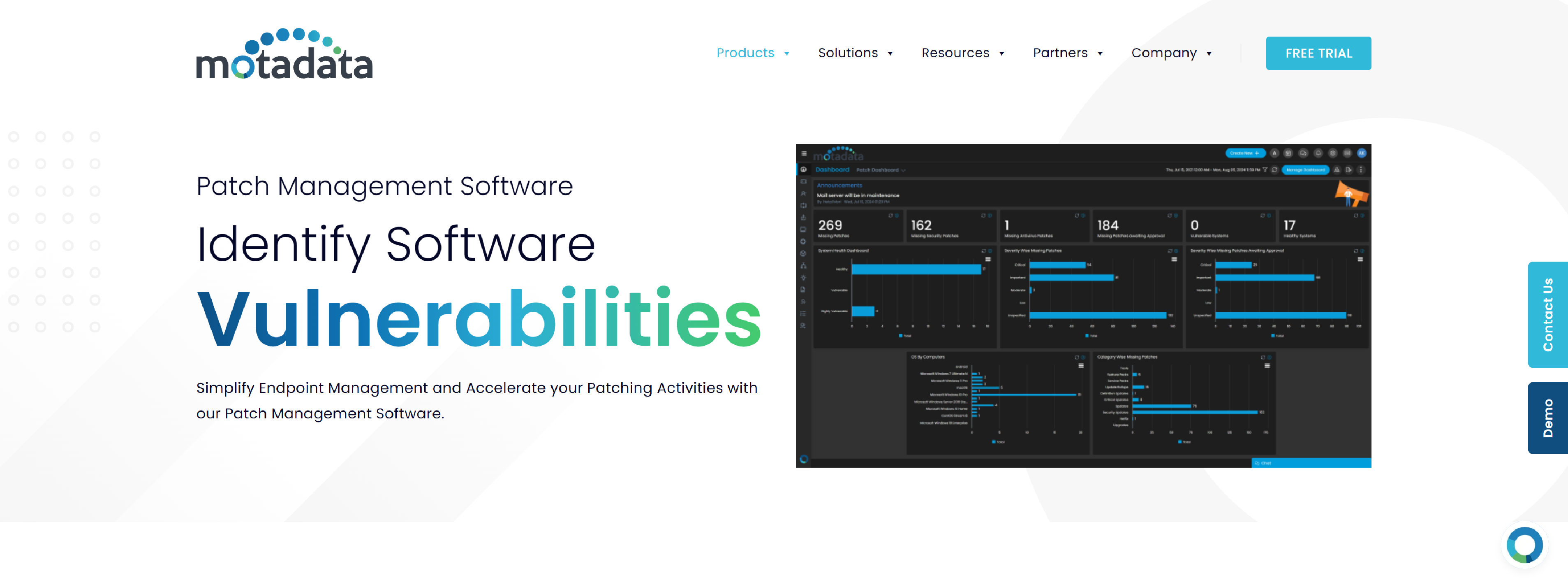
Motadata – Automated multi-OS patch management software that scans and deploys patches across networks based on a predefined policy, with rollback capabilities.
- Recognizing obsolete software or systems that need to be refreshed
- Examining the criticality of patches to identify those requiring urgent focus
- Confirming that patches integrate smoothly with current systems and do not create new problems
- Launching updates on various devices and assessing their effectiveness
Pulseway Automated Patch Management for Operating Systems
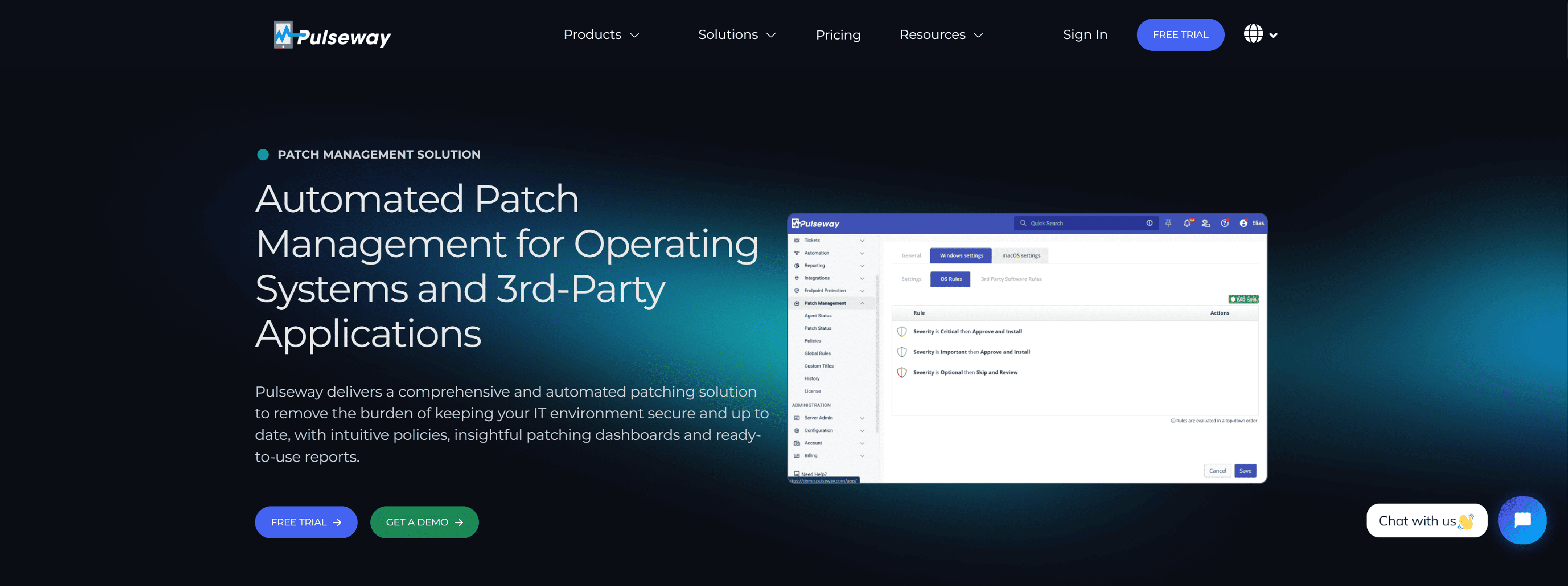
Automatically patch Windows and 3rd Party Applications using Pulseway cutting edge Patch Management module.
- Compliance and Reporting
- Mobile Patch Management
- Patching Workflow Visibility
- Patching Widgets
SysAid Patch Management
Integrated into SysAid IT Asset Management, SysAid Patch Management keeps Windows-based servers and PCs up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Get an overview of all the patches relevant to the active IT assets in your organization
- Customize the automatic SysAid Patch Management policies as needed
- Manually manage patches on multiple or individual assets
- Use a formal change management process, such as recommended by ITIL, to approve patch deployment
- Trace the progress of patch deployments and view the end results
Syxsense Patch Management
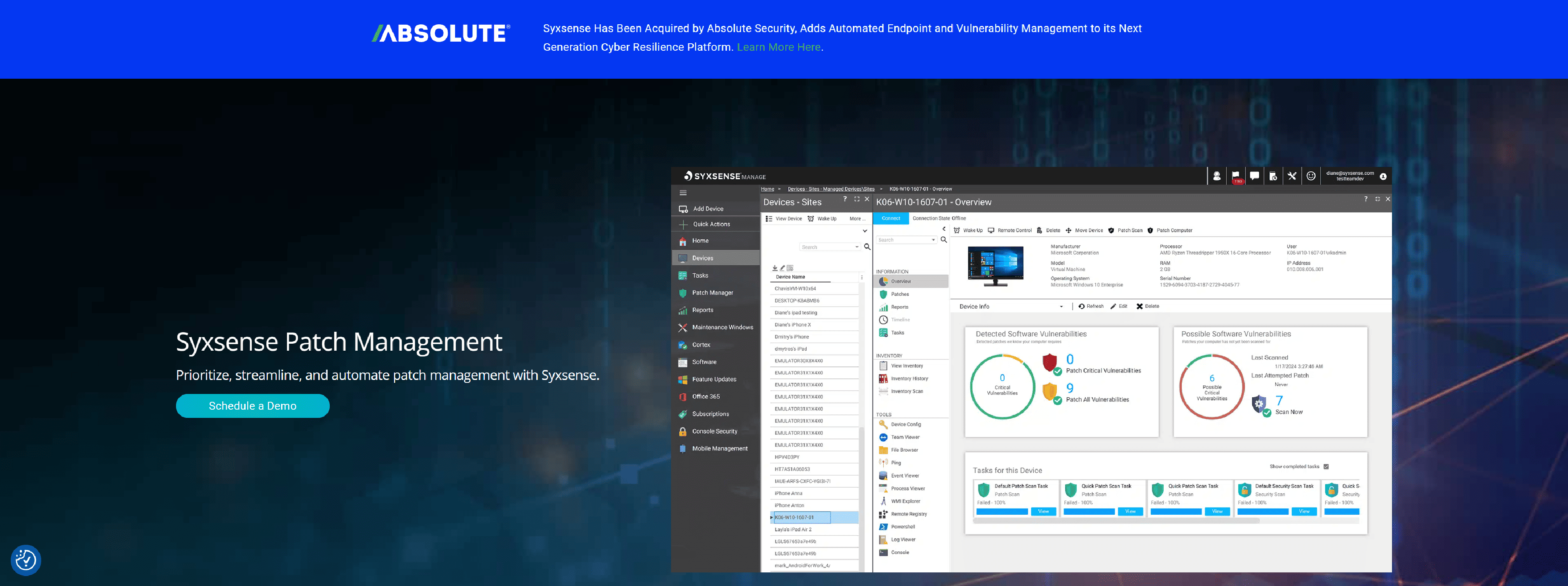
Syxsense Patch Management: Reduce your attack surface and harden devices to lower the risk of security breaches and system downtime caused by software vulnerabilities.
- Patches automatically appear in the console within hours of release
- Patch scans use our sophisticated detection logic to flag vulnerable devices
- Employee productivity is protected by scheduling deployments in recurring Maintenance Windows
Finding the best patch management software
Finding the best patch management software involves understanding the unique needs of your organization and evaluating various factors without focusing on a list of specific solutions.
Identify Your Needs
Start by identifying the requirements specific to your organization, such as:
- Platform Diversity: Do you need to manage patches across multiple operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) and software applications? Consider whether you need cross-platform support or if you only need to focus on a single environment.
- Size of Your Organization: If you’re a small business, you may prefer a simple, cost-effective tool. For large enterprises, you may need a more comprehensive and scalable solution.
- Security & Compliance: If you operate in a regulated industry (healthcare, finance, government), the software should offer strong compliance features, such as detailed reporting, vulnerability management, and auditing.
Automation & Integration Needs
Evaluate the level of automation you require. Automation is key to reducing the manual effort involved in patching, but it’s essential to ensure that the software integrates smoothly with other IT management tools you may already be using, such as:
- IT Service Management (ITSM): If you use tools like ServiceNow, BMC, or Jira, it’s beneficial to choose patch management software that integrates with them.
- Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM): If you’re using RMM tools, look for patch management solutions that work seamlessly with these tools.
- Security Tools: If you have endpoint protection, vulnerability management, or SIEM systems in place, ensure the patch management solution can integrate with them for comprehensive security.
Customization & Flexibility
Look for a solution that allows you to tailor the patch management process to your needs, such as:
- Patch Approval Workflow: Ensure you can control when and which patches are approved for deployment to minimize disruptions.
- Scheduling: Flexibility in scheduling patches to occur during non-peak hours or at times that suit your operational requirements.
- Testing: Some patch management tools allow you to test patches in a controlled environment before wide deployment to avoid issues with production systems.
Security Features
Patch management is primarily focused on improving security, so consider:
- Vulnerability Remediation: The software should not just apply patches but also focus on critical vulnerabilities to prevent exploits.
- Compliance Reporting: If your industry requires specific compliance standards, ensure the software provides robust reporting to demonstrate adherence to those standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS).
Ease of Use and Support
Choose software with an intuitive interface and user-friendly dashboard to simplify patch management tasks, especially if your team is small or lacks specialized IT expertise. Ensure:
- Training & Documentation: Comprehensive guides, tutorials, and ongoing vendor support to help you make the most of the solution.
- Customer Support: Responsive support channels (e.g., 24/7 phone or chat support, dedicated account managers) in case you encounter issues during implementation or operation.
Cost Considerations
Compare pricing models based on the features offered:
- Subscription-based pricing: Typically suited for cloud-based solutions with regular updates.
- One-time fees: May be applicable for on-premise software with fewer ongoing costs.
- Cost vs. Value: Balance cost with the potential benefits, such as reduced manual labor, better security posture, and fewer vulnerabilities.
Trial and Proof of Concept
Many patch management solutions offer free trials or demo versions.
- Test functionality: See how well the solution fits with your existing systems.
- Evaluate ease of use: Ensure the software is intuitive and the deployment process is smooth.
- Monitor performance: Verify how well it handles patch detection, deployment, and reporting.
Vendor Reputation and Reviews
Research user feedback, ratings, and reviews from other companies in your industry or with similar IT environments. Trusted review platforms like CLLAX, G2, TrustRadius, or Capterra provide insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses based on real-world usage.
Types of patch management software
Patch management software can vary based on its deployment methods, the environments it supports, and the range of features it offers. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of patch management software, explained in more detail, without using a list format:
One major distinction is between on-premises and cloud-based patch management software. On-premises patch management is installed and maintained within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It gives IT administrators full control over the patch management process, which is especially important for businesses with specific security or compliance needs. However, it also requires more resources to set up, maintain, and scale. In contrast, cloud-based patch management software operates remotely through the internet, offering greater scalability and ease of use, as it typically requires fewer in-house resources. Cloud-based systems are ideal for organizations with distributed workforces or limited on-site IT staff, as they can be accessed from anywhere and tend to have simpler deployment models. The tradeoff is that businesses may not have as much direct control over the infrastructure and data as they would with on-premises solutions.
Hybrid patch management software, which combines both on-premises and cloud components. This hybrid model provides flexibility for organizations that need to manage patches both locally and remotely. It enables businesses to take advantage of cloud scalability while retaining certain on-premises elements, such as sensitive data handling or specific compliance requirements. Hybrid patch management tools are ideal for large organizations or businesses transitioning to the cloud but still reliant on some legacy systems.
Standalone patch management software is designed specifically to manage patching tasks without additional features like remote monitoring or IT asset management. This software typically focuses purely on detecting, deploying, and reporting patches for operating systems and applications. Standalone tools are great for small or medium-sized businesses that need an efficient patching solution without the complexity of larger IT management suites.
On the other hand, integrated patch management software is part of broader IT management suites, combining patch management with other IT operations, such as remote monitoring, endpoint management, and even security. These integrated solutions allow IT departments to manage multiple aspects of IT infrastructure from a single platform. For enterprises, an integrated approach can provide a comprehensive solution that includes patch management, vulnerability management, IT asset management, and even security incident management, all from one interface.
Software that is security-focused, specifically targeting critical patches that address vulnerabilities. These tools not only apply patches but also prioritize the most urgent security flaws that need immediate attention. Security-focused patch management software is essential for industries with stringent security requirements, like healthcare, finance, and government. It often includes advanced reporting features to demonstrate compliance with security standards and regulations.
Third-party patch management software is designed to handle updates for non-operating system software, such as third-party applications. These tools ensure that applications like Adobe, Java, and browser plugins are regularly updated, which is crucial for closing security holes in third-party programs that can be exploited by attackers. As many patch management solutions focus primarily on operating system updates, third-party patch management tools fill the gap, making them an important addition to any enterprise’s patching strategy.
Each type of patch management software offers different levels of control, flexibility, and automation, depending on the needs of the organization. The choice between on-premises or cloud-based, standalone or integrated, and security-focused or general patch management software depends on factors like the size of the organization, its IT infrastructure, security requirements, and budget.
Why do you need patch management software?
Patch management software is essential because it helps organizations keep their systems secure, stable, and compliant by automating the process of identifying, deploying, and managing patches. Patches fix vulnerabilities in software and operating systems, which are common targets for cyberattacks. Without regular updates, systems become exposed to security threats, performance issues, and legal risks due to non-compliance with industry standards. Patch management also streamlines IT operations, reducing the manual workload of administrators, preventing downtime, and ensuring that critical systems remain protected against emerging threats.
Q&A Patch Management Software
Q: What is patch management software?
A: Patch management software automates the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and applying patches to software and operating systems. These patches address vulnerabilities, bugs, and other issues, ensuring systems remain secure, compliant, and operational.
Q: How does patch management software help with security?
A: By regularly applying patches, the software ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed before they can be exploited by cybercriminals. This reduces the risk of data breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents that could harm an organization’s operations and reputation.
Q: What happens if we don’t use patch management software?
A: Without patch management, patches may be missed, delayed, or applied inconsistently. This can leave systems vulnerable to security threats, increase the risk of downtime, and complicate compliance efforts. Over time, it can lead to inefficient IT operations and higher costs for remediation.
Q: Does patch management software work for all types of software?
A: While many patch management tools focus on operating systems, modern solutions can also handle third-party applications like web browsers, productivity tools, and security software. However, the specific capabilities vary by tool, so it’s important to choose one that meets your organization’s needs.
Q: How often should patch management be done?
A: Ideally, patching should be done as soon as patches are available, particularly for security updates. Many patch management systems allow you to automate the process and schedule patches during off-hours to reduce disruption to business operations.
Q: Can patch management software be automated?
A: Yes, patch management software typically includes automation features that can scan for missing patches, download them, and deploy them to systems without manual intervention.
Q: What are the risks of patch management software?
A: While patch management software greatly enhances security and efficiency, there are potential risks. Patches, if not tested properly, could cause compatibility issues or system crashes. It’s essential to test patches in a staging environment and monitor deployment to mitigate these risks.
Patch management software is more than just a tool for keeping systems up to date; it is a critical element of an organization’s cybersecurity and IT management strategy. By automating the patching process, improving efficiency, and ensuring compliance, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to security vulnerabilities, protect sensitive data, and avoid costly breaches. With the increasing complexity of IT environments and the sophistication of cyber threats in 2025, investing in robust patch management software is no longer optional, it’s a necessity for businesses aiming to maintain a secure, resilient, and compliant IT infrastructure.