Zero Trust security is an approach to cybersecurity that challenges the traditional perimeter security model. Rather than assuming that everything inside an organization’s network is trustworthy, Zero Trust adopts the mindset that nothing should be inherently trusted by default. This strategy emphasizes the importance of verifying and validating every user, device, and transaction, regardless of their location or origin.
The traditional perimeter security model focused on securing the network perimeter with firewalls and other security solutions, treating everything inside the network as safe. However, with the increasing number of sophisticated cyber threats and the rise of cloud computing and remote working, this approach has become outdated and ineffective. Zero Trust aims to address these challenges by implementing rigorous security measures that protect both internal and external resources, regardless of their location.
The central tenet of Zero Trust is the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Instead of granting unrestricted access to internal resources, the Zero Trust approach requires continuous authentication and authorization for every user and device trying to access the network. This is achieved through various technologies and techniques, such as multifactor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and identity and access management (IAM) solutions.
One of the key components of Zero Trust security is micro-segmentation. This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated zones, each with its own access controls and security policies. By implementing micro-segmentation, organizations can limit the lateral movement of cyber threats within the network, reducing the potential impact of a security breach.
Another important aspect of Zero Trust is the adoption of a risk-based approach to security. Instead of treating all users and devices the same, Zero Trust assigns a risk score to each entity based on various factors, such as their location, behavioral patterns, and device health. This allows organizations to apply appropriate security controls based on the risk profile of the user or device, reducing unnecessary friction for legitimate users while maintaining a high level of security.
Zero Trust also emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and visibility. Organizations need to have real-time visibility into the activities and behaviors of users and devices within their network. This enables them to detect and respond to threats in a timely manner, reducing the dwell time of attackers and minimizing the potential damage.
Implementing Zero Trust security requires a holistic approach that encompasses people, processes, and technology. It involves aligning security policies and practices with the Zero Trust principles, educating users about the new security measures, and leveraging a wide range of security technologies, such as endpoint protection, network segmentation, and threat intelligence.
The benefits of Zero Trust security are numerous. By assuming that nothing should be inherently trusted, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and data loss. Zero Trust also enables organizations to achieve granular access controls, ensuring that users and devices only have access to the resources they need for their specific roles. This not only improves security but also enhances compliance with various regulatory requirements.
Zero Trust security is a paradigm shift in the approach to cybersecurity. It challenges the traditional perimeter security model by assuming that nothing should be trusted by default and requires continuous verification and validation of every entity accessing the network. By implementing Zero Trust principles, organizations can improve their overall security posture and better protect their data and resources in today’s evolving threat landscape.
Top 12 Best Zero Trust Security Solution Providers
HASHICORP
HashiCorp delivers consistent workflows to provision, secure, connect, and run any infrastructure for any application.
Enable scalable, dynamic security across clouds
- Improve enterprise security posture
- Reduce the likelihood of a breach
- Accelerate secure multi-cloud adoption
Adopt Zero Trust Security across clouds with these four pillars
- Machine authentication & authorization
- Machine-to-machine access
- Human access and authorization
- Human-to-machine access
AKAMAI
Akamai Connected Cloud keeps applications and experiences closer to users and threats farther away.
- Strengthen your security posture
- Free up your security team to focus on business
- Gain insight on emerging threats
ZSCALER
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange, the true zero trust platform securely connects users, workloads and devices against exposure to corporate networks.
- Protect against cyberthreats and data loss
- Provide fast, direct, and secure app access and digital experience monitoring
- Eliminate management overhead and the cost of point products and appliances
NETSKOPE
Netskope empowers the largest organizations in the world with the right balance of protection and speed they need to enable business velocity and secure their digital transformation journey.
- Accelerated business agility
- Security without performance trade-offs
- Reduced security risk
- Improved security posture
- Reduce total cost of operations
F5
F5 Distributed Cloud platform delivers improved functionality, advanced security, and more simplified operations than native services from cloud providers.
- Continuously review and assess access, threats, and trust
- Provide visibility into application access and traffic trends, aggregate data for long-term forensics, accelerate incident responses, and identify issues and unanticipated problems before they can occur
- Initiate quick action, if required, including the termination of specific access sessions
- Deliver a fast overview of access health
DUO
Duo protect your workforce and user data from cybersecurity risks with Multifactor Authentication (MFA), Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and a Single Sign-On solution.
- Security Overload for End-Users
- Workforce Decentralization
- Environmental Complexity
- Streamline User Experiences
- Protect a Diverse Workforce
- Secure Remote Work
SOLO.IO
Solo.io Industry’s Leading Cloud-native Networking Platform for APIs, Containers and Cloud Built on Kubernetes, Istio, Envoy, GraphQL and Cilium
- Zero trust security for APIs and application ingress with an API Gateway
- Zero trust security for distributed applications with a service mesh
Citrix DaaS, Citrix Secure Private Access, Citrix Analytics for Security
Citrix workspace software delivers the business technology that creates a simple, secure and better way to work from anywhere and on any device.
- Assessing existing cybersecurity controls and determining the key network flows and vulnerabilities
- Determining a protected surface that will be shielded from harm through zero trust measures
- Implementing specific technologies such as adaptive and multifactor authentication, VPN-less proxies, and secure embedded browsers
- Continuously monitoring the network to keep tabs on suspicious activity and fine-tune the solution mix and overall cybersecurity approach as needed
FORTINET
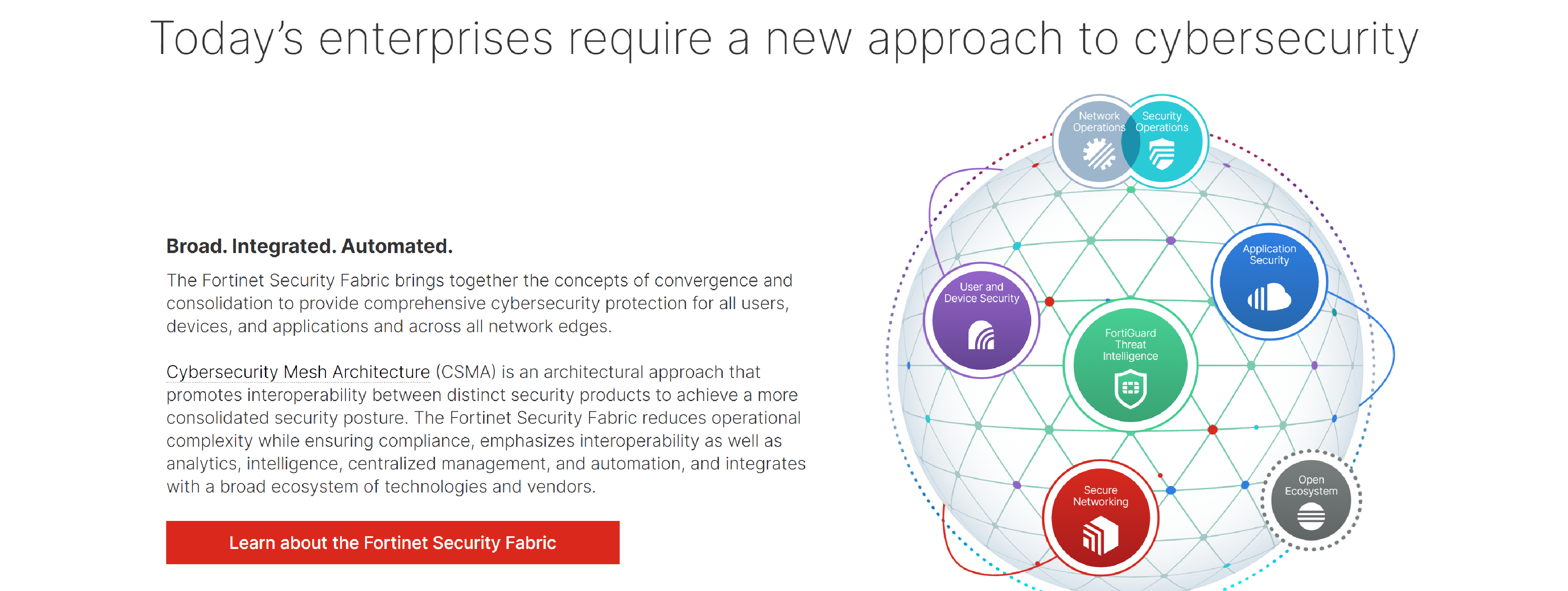
Fortinet Universal ZTNA provides secure and simple access to applications, regardless where they are located, for users working from anywhere.
- Enables ZTNA policies to be enforced for both remote workers and on-site workers
- Grants access to a specific application only for that session
- Verifies the user identity, the device identity and posture, before granting access to an application
- Provides both secure access and endpoint protection with a single, unified agent
- Allows moving from VPN to ZTNA over time, as a free feature of FortiOS 7.0 and above
- Establishes TLS encryption automatically between endpoint and access proxy, hiding traffic
LOGRHYTHM
LogRhythm SIEM platform effectively unifies log management, security analytics, case management, and incident response.
- Detect Threats Earlier and Faster
- Gain Visibility Across Your Environment
- Easy to Use
- Build for Today, Scale for Tomorrow
YUBICO

Yubikeys enable phishing-resistant user identity verification before providing access.
- Accelerate Zero Trust with strong authentication
- Trusted user identity using phishing-resistant modern MFA
- Build a great user experience with passwordless that drives productivity
OKTA
Okta’s identity platform is easy-to-use, neutral, and works with your existing solutions, so you’re free to choose the best technology for now and the future.
What are the main Zero Trust best practices?
1. Implement robust identity and access management (IAM) systems: One of the fundamental principles of Zero Trust is to verify and validate every user and device seeking access to the network. Implementing IAM systems that employ strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and adaptive access controls helps ensure that only authorized individuals are granted access.
2. Segment the network: Network segmentation plays a crucial role in Zero Trust. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments and applying access controls based on user or device identity, organizations can minimize the lateral movement of threats and contain potential breaches. This segmentation can be achieved using virtual local area networks (VLANs), software-defined networking (SDN), or other network isolation techniques.
3. Apply the principle of least privilege (PoLP): Following the PoLP ensures that users and devices are only given the minimum amount of access necessary to perform their tasks. This practice helps prevent privilege escalation attacks and restricts the potential impact of compromised credentials or devices.
4. Continuous monitoring and visibility: Zero Trust requires organizations to have real-time visibility into their network endpoints, user activities, and data flows. By continuously monitoring and analyzing network traffic and behaviors, organizations can quickly detect and respond to any anomalous activities or potential security incidents. Tools such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), and Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) solutions can be employed to achieve this level of visibility.
5. Embrace micro-segmentation and granular access controls: Traditional network security models operate based on perimeter defenses. Zero Trust, on the other hand, focuses on segmenting the network and applying granular access controls. By implementing micro-segmentation and enforcing security policies on a per-application or per-workload basis, organizations can minimize attack surfaces and limit the impact of any potential breaches.
6. Adopt a continuous authentication model: In Zero Trust, authentication does not happen just once during the initial login. Instead, continuous authentication techniques are employed to verify user or device identity at various stages throughout the session. This can include analyzing user behavior, contextual factors, and device posture to ensure that the access is still authorized and the user or device has not been compromised.
7. Encrypt all sensitive data: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit is a core component of a Zero Trust strategy. Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot read or use it without the correct decryption keys.
8. Regularly audit and review access controls: Organizations should conduct regular audits of their access controls to ensure that they remain effective and aligned with the organization’s policies. These audits can help identify any potential gaps or misconfigurations that may lead to unauthorized access.
9. Emphasize user education and awareness: Zero Trust is not just about technology; it also requires a cultural shift and user involvement. Regular training and awareness programs can help educate users about the importance of following security best practices, such as recognizing and reporting phishing attempts, selecting strong passwords, and keeping their devices updated.
10. Regularly update and patch all systems: Keeping all systems and software up to date with the latest patches and security updates is crucial to maintaining a secure Zero Trust environment. Regular vulnerability scans and patch management processes should be implemented to identify and remediate any vulnerabilities promptly.
By following these best practices, organizations can establish a robust Zero Trust framework that enhances their overall security posture and reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.