If you were to ask 10 corporate leaders what CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is, you would likely get 10 different definitions. Some would say CRM is “improving customer contact”, others would say “understanding customer needs”. Where as these may be some of the desired results, they fail to encompass the true definition.
In the broadest sense, CRM is a business philosophy that places customer needs as the most important focal point for a business organization. In the post WWII era, companies flourished because they made something of value – anything. Production capacity was most important. During the technology revolution of the 70’s and into the 90’s, product innovation became the most important drivers. More advanced products, whether perceived or real, drove sales.
But the market has changed. Now, customers have more product choices than ever. It is no wonder that customer loyalty is declining. For these reasons many corporation now consider CRM their primary focus – a focus that at its core attempts to maximize every sales opportunity and optimize every customer’s purchase and ownership experience.
Ultimate customer satisfaction seems like a very lofty goal. As with all esoteric concepts, putting CRM theory into practice is the hard part. Applying CRM involves three primary ingredients.
|
Professional people |
Professional people interact with customers to either assess and/or respond to customer needs. |
| Well-designed processes | The interaction with customers provides information that is processed within an organization. |
| Functional technology | Technology makes critical information available on a timely basis to every department of the organization that has some form of customer contact for the purpose of make smarter business choices. |
The first 2 ingredients (Professional people and well-designed processes) are not new. Long before CRM became popular, good business practices included these principals. What has change is Functional technology.
CRM Technology Evolution
CRM technology has its roots in the early 70’s when computers were making their way into the corporate environment. These mini computers were used primarily for order processing/call center tasks. They were expensive and required lots of program customization. But it was not till the 80’s when the desktop PC gained popularity that “shrink wrapped” CRM software tools first hit the market. These products were a combination PIM (Personal Information Managers) that managed daily calendar tasks and contact management functions.
From the early 80 there were 2 different platforms for CRM solutions:
- Server based:
Software and data resided on a server so that all those connected to the LAN could enter and view data. These were designed for large corporations, typically over 1 billion in revenue such as the global 3,500 corporations. In the early days, Vantive, Scopus, Clarify and Siebel were among the dominant suppliers.
- Client based:
Software and data resided on a desktop or notebook PC most typically in a MS Windows OS. The advent of the PC and subsequent portability of notebook PCs made these products ideal for mid and smaller organizations.
In the early days, both platform solutions focused on 3 primary missions:
- Sales Force Automation
- Marketing Automation
- Field Service Automation
Why: because this was the area of highest pain level as well and the business components that could benefit the most.
The client based solutions evolved as the PC market evolved. With minor exception, these products were designed for a single PC (client-based) and were contact-centric. These affordable products were an important first step and offered users a manageable way of organizing their sales contact information, appointments and sales notes.
As important as these first generation products were, they failed to make information available to management and other organization departments. And, these products were designed to focus on contacts rather than contacts as part of a customer organization.
Later generations added more features. The most important was the ability to easily view all the contacts within a customer company. And, sales forecasting features were included. But the client-based design restricted sharing of the data throughout the organization. It wasn’t until these programs developed enterprise versions that the information was available to others who were connected to the organizations local network (LAN).
But enterprise versions created as many problems as they solved. Remote users were required to synchronize their data over VPN (Virtual Private Network) modem connections. If the connection was unstable, data was lost or worse – corrupted rendering the database for that PC useless until it was restored. Furthermore, a full version of the program was required for each user PC. Although this enabled users to work off-line, it added IT maintenance costs.
CRM Components
Customer Relations Management (CRM) is a challenging goal for any size organization:
Sales automation streamlines the sales process and helps salespeople and their supervisors manage both customers and the sales cycle through such applications as contact managers, opportunity or pipeline managers, configurators, and order entry.
Marketing automation is a set of applications that help marketers manage and simplify the marketing process. Applications include campaign management; email marketing, database marketing and data marts, and marketing encyclopedias.
Customer Service/Call Centers: Call centers are the primary conduits between consumers and corporations. Customer Service is the primary business process for creating customer loyalty, promoting customer retention, and ultimately increasing customer value while reducing cost of sales.
Analytics covers the process of extrapolating true business intelligence from disparate customer data sources in order to segment, analyze, and serve the consumer in the most efficient manner possible. Additionally, analytics is also getting predictive, empowering businesses to identify how a customer is likely to respond to different sales and marketing campaigns.
Channel Management is the process of extending an enterprise’s internal knowledge resources and business processes to its suppliers and partners outside the company’s intranet. Most typically channel management is used to describe the way a company interacts with its sales channel but its definition can also be extended to other partner relationships beyond the sales process. Applications and solutions are designed for streamlining and automating the back end/supply chain processes.
Integration involves tying together CRM applications with other IT systems inside either a mid-market company or an enterprise environment. This can include integrating with current ERP systems, databases, Internet and intranet applications, human resources and employee management software and partner and supply chain systems.
CRM Implementation Considerations
There are 2 primary implementation philosophies:
- Organization wide
- Task Specific
The organization wide approach embraces CRM at every level of the organization. Sophisticated technology is integrated into legacy systems to capture customer information from every source. Employees must be thoroughly trained to understand the complexities of these software tools and how to use them.
Organization wide tools integrate a variety of CRM components:
- Contact Center
- Sales force Automation
- Field Service Automations
- Marketing Automation
- Electronic Commerce
- Self-Service Customer Support
- Reporting
Such systems can cost into the millions of dollars and require months if not years to fully integrate into legacy business systems.
The task specific approach addresses synergistic components of CRM and is more sales and marketing focused.
- Contact Management
- Sales force Automation
- Marketing Automation
- Reporting
By their very design, task specific CRM solutions are less complex and easier to integrate. Although these CRM tools are offered in both client/enterprise and ASP models, the ASP model offers lower ownership costs and may be applied to independent sales agency / dealer sales models.
Choosing the Right CRM Tools
CRM helps companies develop successful strategies based on a true understanding of customer needs, market developments and competitors. Choosing the right CRM tools depends on the organization needs, budget and implementation factors.
Larger, multi-national organizations may choose to hire consultants specializing in CRM where as small and mid size organizations may choose to assign a management team.
Special attention should be given to the area of integration and process issues. As CRM solutions increase in their scope, the more likely that standard organizational processes will need to be overhauled. Likewise, CRM tools that are more specific in nature require less integration and fewer disruptions in current processes.
The best CRM solutions are those that are characterized by:
Simplicity – Some CRM solutions providers are creating complicated software mega-solutions. Where as these solutions may seem to address a multitude of CRM issues, they are often so complex that the solution is worse than the issues. Choosing a solution that offers an intuitive user interface and is easy to use is a strong success criterion.
Affordability – Bells and whistles never come cheap. In addition to “feature bloat”, the price tag of may CRM solutions can quickly skyrocket into the millions of dollars. Solutions can range from a low of $50/user per month to well into the $100s/user per month.
Robust Search Functionality – Tracking sales leads and opportunities is only part of the equation in a successful sales and marketing strategy. These efforts mean little if you don’t have the tools to measure the results. CRM solutions that offer customizable reporting and filtering allow management to conduct business more effectively and efficiently.
Flexibility – CRM solutions must be able to adapt to the way you conduct your business, not the other way around. Look for subtle capabilities like custom labels and private labeling of the software interface. Users will be more apt to make the most of the system when it looks and feels like your company. Data collection, presentation and reporting must be flexible enough to accommodate vertical markets.
Organization benefits will differ widely depending upon the market served and the type of organization (production, research, service, etc). As a guideline, consider this list of benefits as your starting point
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Improved market share
- Increased revenues
- Increased profit margin
- Real time access to customer information, account history, order information etc.
- Improved response time to requests for information. Ability to meet customer requirements increased
- Reduced costs of using and buying services and products
- Reduced expense of customer handling, e.g., lower call center expense
By applying benchmarking techniques, current vs. future CRM benefits may be quantified to assist in the CRM solutions decision-making process.
ENGAGEBAY
EngageBay is an affordable all-in-one marketing, sales and service software for growing companies to engage web visitors and convert to happy customers.
- Simple Contact Management
- Nurture Leads
- Automated tasks & Appointment scheduling
- Make Calls from CRM
- Enhance sales efficiency using automation
- CRM Analytics
- Sales Gamification
- Custom Reports
SutiCRM

SutiCRM is cloud-based customer relationship management software that automates the processes of marketing, sales, support, and contracts from a single multi-sided platform(MSP).
- Marketing Automation
- Sales Force Automation
- Reporting and Analytics
- Customization
- Social CRM
- Customer Account Management
AGILECRM
Agile CRM Software is the best, easy, powerful yet affordable Customer Relationship Management (CRM) with sales and marketing automation for small businesses.
- Integrated Marketing Automation
- Engage More Leads
- Real-Time Alerts and Notifications
- Robust Social Media Marketing
- 360-Degree Contact View
- Personalized Outreach
- Everything Updated in Real Time
REALLYSIMPLESYSTEMS

ReallySimpless easy to use cloud-based CRM software is designed specifically for small businesses B2B. It includes everything you need to run your sales and marketing.
- Sales automation
- Reporting
- Custom crm
- Customer support
- Security
- Integrations
- Marketing modules
- Service desk modules
SALESFORCE

Build more meaningful and lasting relationships and connect with your customers across sales, customer service, marketing, communities, apps, analytics, and more using our Customer Success Platform.
- World’s most trusted solution and #1 CRM according to IDC
- A scalable, customizable, future-proof platform with built-in AI and automatic upgrades
- Enterprise-level security and ongoing support to help you grow
- An app ecosystem that means you get more from apps you already use
ZOHO
Run your entire business with Zoho’s suite of online productivity tools and SaaS applications. Over 40 million users trust us worldwide.
SALESMATE
Sales CRM Software for small businesses with easy to use and intuitive interface. Give Salesmate CRM Software a free trial without long-term commitments.
- Organize your contacts
- Sales reporting
- Customer segmentation
- Sales automation
- Effective forecasting
- Activity tracking
SAGE
Sage CRM software and tools for small businesses increase productivity and efficiency and unlocks hidden revenue for your business.
- Centralize your critical business information
- Automate sales
- Launch targeted marketing campaigns
- Provide world-class customer service
- Gain insights into your business
- Manage your contacts
1CRM
Designed for small to medium-sized businesses, 1CRM is the All-in-One CRM solution for sales tracking, marketing automation, PSA, order management & more!
- Lead Capture
- Automated Follow-ups
- Generated Reports
- Smart Replies
- Knowledge Base
- Easy Reminders
ACT

Purpose-built for small businesses, Act! combines proven CRM with powerful Marketing Automation, providing you with the ultimate toolset to drive business growth.
- Powerful sales & marketing features to fuel growth
- Freedom to tailor an Act! experience to fit your needs
- Flexible Cloud, on-premises, & hybrid deployments
- Member benefits to keep current, covered, & connected
- Extensive online resources to get the most from Act!
- Convenient phone, live chat, & email support options1
ALLCLIENTS
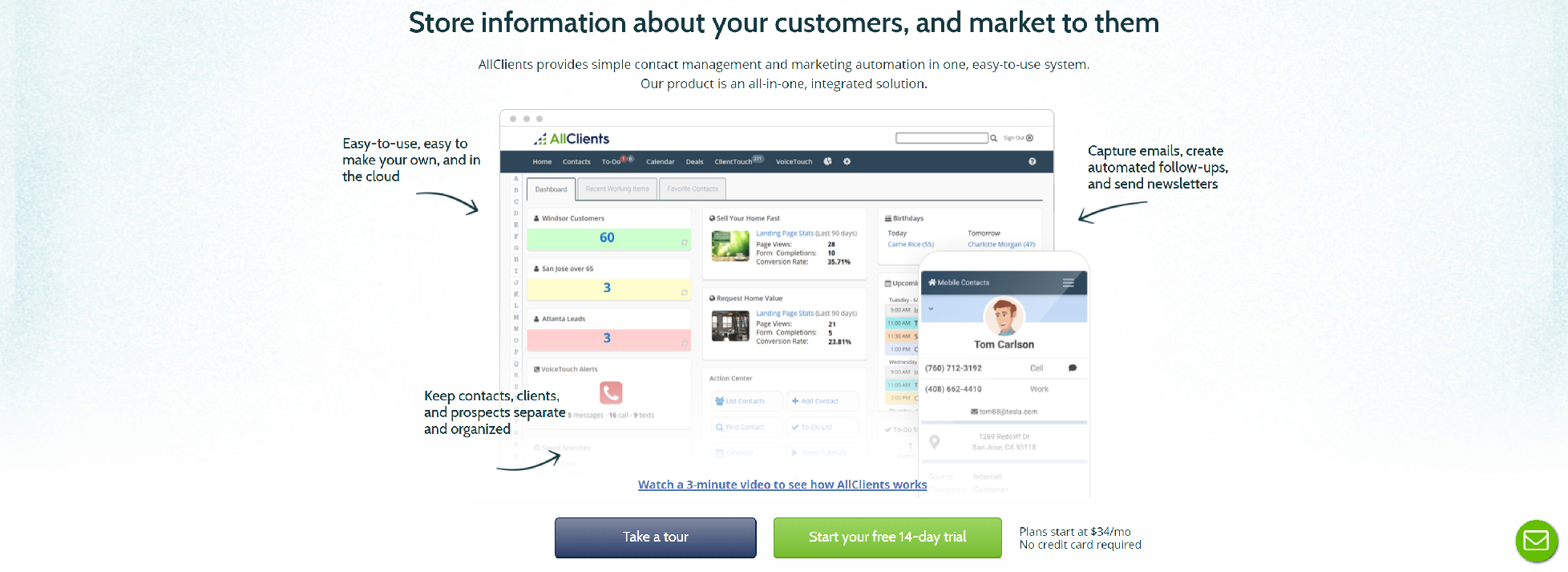
AllClients is an easy-to-use web-based CRM software and marketing automation system. Features include recorded message systems, email campaigns and more.
- CRM
- Workflows
- Funnels
- Opt-In Email with Beautiful, Responsive Templates
- Landing Pages
- Autoresponders
- Free Recorded Message System
- Text-to-Join
- Monthly newsletter
- Teams
- Pipeline Deals
SELLUTION
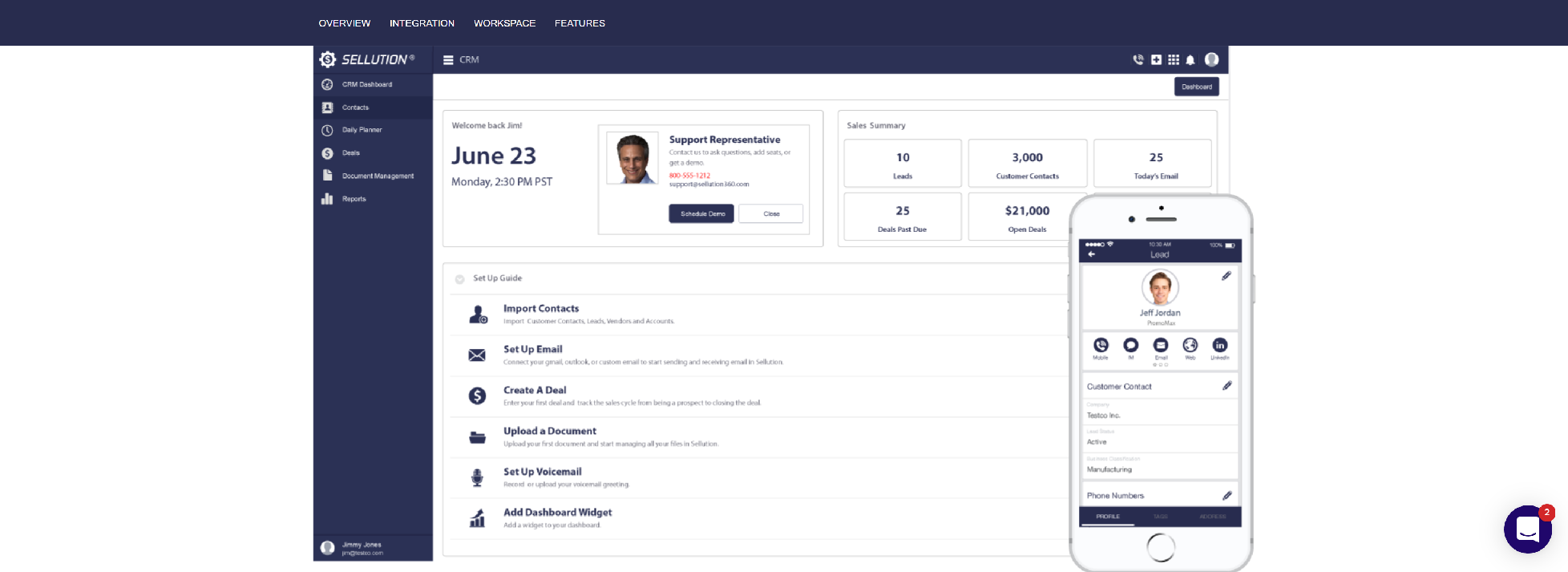
Sellution combines Ecommerce, CRM, Marketing Automation, & Customer Service tools into one system so small businesses can unify their data and create winning customer experiences.
- Contact Management
- Security
- Dashboards
- Mobile CRM
- Voice
- Smart Reporting
CLINCHPAD
An online sales CRM software, built for small teams that helps you track and organize leads through an easy to use visual interface.
- Visualize your sales pipeline
- Collaborate with your team
- Manage your contacts and organizations
- Categorize your leads by products, sources and zones
- Attach emails to leads
- Integrations
- Reports
- Security and Reliability