Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software is a set of tools and processes designed to prevent sensitive data from being lost, misused, or accessed by unauthorized users. DLP software helps organizations protect confidential information such as financial data, intellectual property, customer details, and personal identifiable information (PII) from accidental or intentional breaches.
Discover the top 15 Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software solutions
Forcepoint
Forcepoint Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is an enterprise solution that prevents data exfiltration across all channels, including cloud, email and endpoint.
- Monitor and block security incidents in real time wherever users interact with data
- Streamline policy configuration and management with 1,700+ classifiers and policy templates to identify and secure PII and PHI
- Contextualize user behavior to forecast risk and automatically adjust policies to prevent security before they happen
- Create, manage and report on policies for cloud, web, email and endpoint from one platform and dashboard
Checkpoint
Check Point Data Loss Prevention (DLP) pre-emptively protects your business from unintentional loss of valuable and sensitive information.
- Tracks and controls any type or format of sensitive information in motion, such as e-mail, web browsing and file sharing services
- Educates and alerts end-users on proper data handling without involving IT/security teams, and allows for real-time user remediation
- Centrally managed across your entire IT infrastructure from a single console
Endpointprotector
Endpoint Protector is the only truly multi-OS DLP solution to offer real-time data protection across Windows, macOS and Linux endpoints, even when they’re offline.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII) Protection
- Insider Threat Protection
- Compliance and Regulations
Kickidler
Kickidler’s advanced data loss prevention software provides a robust solution to protect your valuable information.
- Insider Threat Prevention
- Data Misconduct Detection
- User Behavior Analytics
- Continuous Data Monitoring
- Employee Monitoring
Solarwinds
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager provides provisioning, deprovisioning, and access rights auditing.
- Automate User Access Policy, Analysis, and Enforcement with Data Loss Prevention Tools
- Quickly Investigate Suspicious Activity Alerts
- Capture User Access Details to Investigate Insider Risks and Improve Data Leakage Prevention
- Use Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Capability to Validate Compliance in Data Protection
Cloudflare
Cloudflare – Secure hybrid work, defend against threats, protect your data, and simplify any-to-any connectivity on your path to consolidation.
- Verify more types of identify context and more easily adapt policies
- Block more threats using our peerless threat intelligence
- Improve visibility into sensitive data, security compliance, and user experiences
- Expand your deployment with our flexible architecture and single-pass inspection
Safetica
Safetica protects companies agains data loss, with data loss prevention and regulatory compliance.
- Gain data visibility and discover sensitive data
- Protect sensitive and business-critical data
- Empower users to work with sensitive data and promote security awareness
- Detect and mitigate regulatory compliance violations
Cloud.google
Cloud.google – enables enterprises to automatically discover, classify, and protect their most sensitive data elements.
- Take charge of your data on or off cloud
- Gain visibility into sensitive data risk across your entire organization
- Reduce data risk with obfuscation and de-identification methods like masking and tokenization
- Seamlessly inspect and transform structured and unstructured data
Code42
Code42 Incydr is a SaaS data protection solution that sees and stops data leak and theft in one platform, without creating extra work for security.
- See data exfiltration without managing complex policies
- Respond to data leaks based on the exact incident
- Less work for you to secure data & stay compliant
Spin
SpinOne’s Data loss prevention (DLP) capability is a critical component of cybersecurity strategy in Google Workspace, Microsoft O365, Salesforce and Slack.
- Secure, Compliance Friendly Backup
- Fast, Accurate Backup & Recovery for a Strong DRP
- SpinBackup
Versa-networks
Versa’s Network DLP functions being offered as part of comprehensive security offering VSPIA makes it simple and effective for Enterprises to purchase and use Versa’s Network DLP functionalities together with the rest of comprehensive security capabilities provided by Versa’s VSIA offering.
- Comprehensive Coverage
- Powerful Policy Actions
- Single Policy definition / language and policy engine
- CASB and Network DLP Working Together for Best Data Protection
- Easy to Use
- Regulatory Compliance
Proofpoint
Proofpoint modern, human-centric approach to identify and mitigate risks before a data breach happens.
- Quickly detect and resolve data loss risk across email, cloud and endpoints
- Deploy quickly, scale automatically and maintain with ease
- Prevent data loss with user behavior and data detection
Teramind
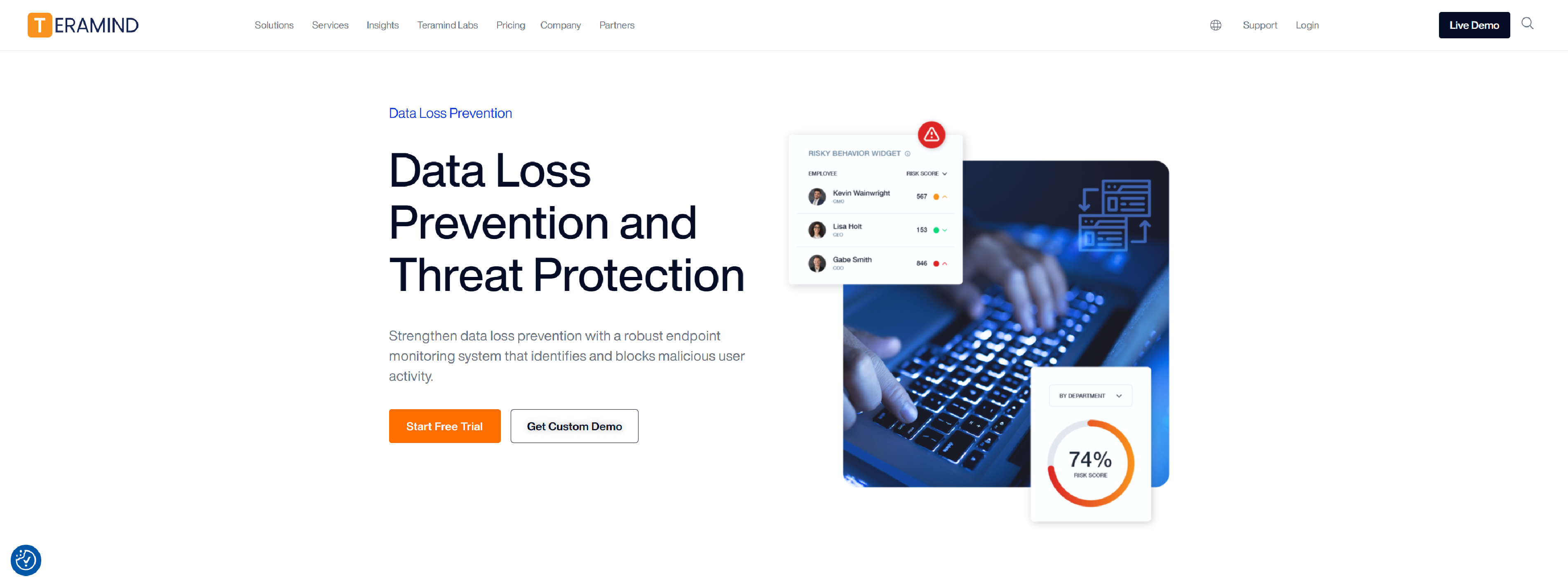
Teramind – Strengthen data loss prevention with a robust endpoint monitoring system that identifies and blocks malicious user activity.
- Time-Stamped Screen Recordings
- Smart Rules & Automated Responses
- Online Meeting Monitoring
- Website & Application Monitoring
- Remote Desktop Control
- Optical Character Recognition
- Keystroke Logging
Zscaler
Zscaler Data Loss Prevention (DLP) protects data and intellectual property for global enterprises, get real-time reports and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Secure internet, email, endpoint, IaaS, private apps, and risk posture in one simple platform
- Quickly scale DLP to emails and attachments without configuration changes via SMTP relay
- Easily find data risks with AI-powered data discovery across endpoint, inline, and clouds
Metomic
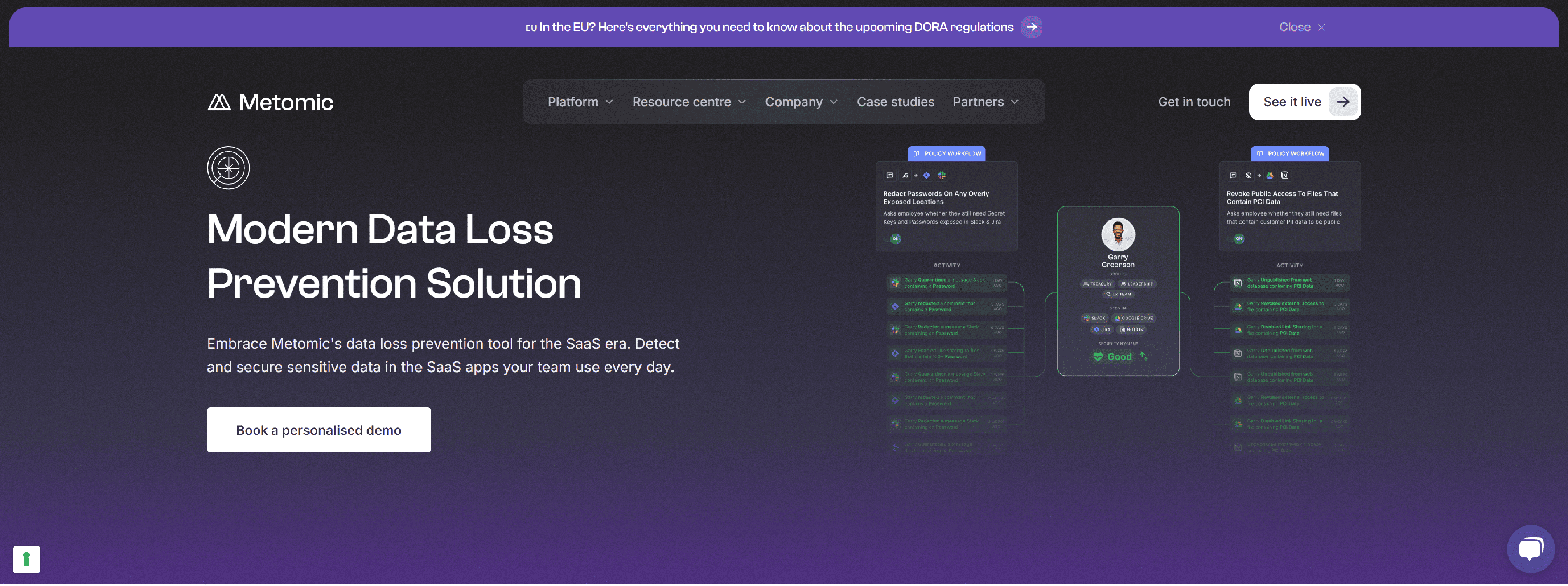
Metomic’s human-centric data security solution integrates instantly with your SaaS apps to help you detect, protect and secure sensitive data hiding in your SaaS apps.
- Automatically redact sensitive data when it’s shared in the wrong place at the wrong time
- Retain data for a set period of time to minimise risk, without getting in the way
- Notify your team, or employees directly, when sensitive data risks appear in your SaaS applications
Open Source Data Loss Prevention Tools
Open Source Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software refers to freely available software tools designed to monitor and protect sensitive data within an organization, preventing unauthorized access, misuse, or loss.
OpenDLP
OpenDLP (Open Data Loss Prevention) is an open-source software tool designed to help organizations identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data across their IT environments. Its primary purpose is to detect and prevent data leaks or unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property.
MyDLP
MyDLP is an open-source Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution designed to help organizations safeguard sensitive data and prevent its unauthorized access, leakage, or loss. Like other DLP tools, MyDLP focuses on identifying and monitoring sensitive data across various systems, such as endpoints, networks, and storage locations.
Understanding the Dynamics of Data Loss Prevention
Understanding the Dynamics of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) involves exploring how the technology functions, its key components, and the different strategies and processes used to protect sensitive data from being exposed, leaked, or stolen.
Types of DLP Solutions
DLP solutions vary depending on where they focus their protection efforts.
- Network DLP: Protects data as it travels across the network, monitoring for sensitive information being sent out via email, file transfers, or web applications. It helps prevent data leaks over communication channels.
- Endpoint DLP: Focuses on protecting data on individual devices, such as laptops, desktops, or mobile devices. This type of DLP monitors activities like file copy, printing, USB device access, and other potential endpoints where data can be lost or copied.
- Storage DLP: Monitors data stored on servers, databases, and cloud environments to prevent unauthorized access or data being stored in places where it shouldn’t be.
Key DLP Technologies and Methods
DLP solutions use several key techniques to monitor and control sensitive data:
- Content Inspection and Fingerprinting: DLP systems can scan and analyze the content of files, emails, and data being transferred. They can identify specific patterns or “fingerprints” related to sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers, social security numbers, proprietary company data).
- Contextual Analysis: DLP systems assess the context in which data is being accessed, used, or transferred. For example, it may recognize that sending sensitive information to an external recipient without encryption violates company policy.
- Keyword and Data Pattern Matching: DLP uses predefined keywords or regular expressions (e.g., email addresses, financial numbers) to detect and protect sensitive information based on recognizable patterns or phrases.
- Behavioral Analytics: By analyzing user behavior and access patterns, DLP can detect unusual activities that may suggest malicious intent or a data breach.
Policy Creation and Management
One of the key components of DLP is establishing policies that define what constitutes sensitive data and how it should be handled.
- What data should be protected: This includes financial data, PII, intellectual property, trade secrets, or any other data the organization deems sensitive.
- Where the data can be shared or accessed: Policies will define who has access to sensitive data and under what circumstances.
- How to enforce security measures: This could involve blocking the transfer of data, encryption, or alerting security teams if the rules are violated.
Policy management is essential for customizing DLP software to meet an organization’s specific data protection needs.
DLP Enforcement Methods
Enforcement is where DLP takes action based on detected incidents or policy violations.
- Block: Prevent the transfer, sharing, or access of sensitive data, either in real time or after an action is flagged.
- Alert: Notify administrators or security teams that a violation has occurred, enabling them to take manual action.
- Encrypt: Automatically encrypt sensitive data before it is sent over an unsecured channel, such as email or over the internet.
- Monitor: Track user activities involving sensitive data to create audit trails, and then report on suspicious actions.
User Education and Behavior
While DLP software can enforce rules, human behavior remains a significant factor. A successful DLP strategy integrates user training to ensure staff members understand the importance of data protection and the policies in place.
Insider Threats: DLP not only guards against external breaches but also helps protect against malicious or negligent behavior from insiders. Educating users about DLP policies and their consequences is key to minimizing human error, which is a leading cause of data leaks.
Incident Detection and Response
DLP systems are designed to detect potential data breaches or violations of policies.
- Incident Logging: The system records details of the incident, creating a log that can be used for analysis or auditing.
- Alerting: Notifications are sent to security personnel or administrators to investigate the incident.
- Remediation: Depending on the severity of the breach, DLP systems can trigger automatic remediation measures such as blocking data transfers or quarantining compromised files.
This quick detection and response are essential in mitigating damage and preventing large-scale data breaches.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance is a crucial aspect of DLP. Many industries, such as healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI-DSS), and government (FISMA), have stringent regulations around data protection. DLP helps organizations stay compliant by ensuring that sensitive data is handled according to legal requirements and that any potential violations are quickly detected and addressed.
Audit Trails: DLP solutions create audit trails that document who accessed sensitive data, when, and what actions were taken.
Challenges in Data Loss Prevention
While DLP offers many benefits, it also comes with its challenges:
- False Positives: DLP systems might flag non-sensitive data as sensitive (false positives), leading to unnecessary alerts and potentially disrupting legitimate business activities.
- Data Encryption: While encryption is a powerful DLP tool, it can sometimes complicate workflows, especially if data needs to be accessible for legitimate business operations.
- User Resistance: Employees may feel that DLP tools restrict their freedom to perform their work. Striking a balance between protecting data and enabling productivity is essential.
- Complex Configuration: Setting up DLP policies and fine-tuning them to avoid both data loss and business disruption can be complex and time-consuming.
The dynamics of Data Loss Prevention involve a complex interplay of monitoring, policy enforcement, and incident response to safeguard sensitive information.
Key Considerations for Implementing DLP Successfully
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) successfully requires a thoughtful approach that aligns with your organization’s data protection needs and business goals. First, it’s essential to define what sensitive data needs protection, considering the types of data, such as personal, financial, or intellectual property. Clear policies must be created to guide how sensitive data is handled and what actions should be taken if a violation occurs.
To avoid disrupting business productivity, it’s important to balance security with operational efficiency. Fine-tuning DLP settings to minimize false positives ensures that legitimate business activities aren’t unnecessarily flagged. Additionally, integrating DLP with other security measures like encryption, endpoint protection, and network monitoring enhances overall data protection.
Employee education plays a crucial role. Workers must be informed about the new policies, the purpose of DLP, and the potential consequences of policy violations. Finally, continuous monitoring, review, and adaptation of the DLP system are necessary to keep pace with evolving business needs, new technologies, and emerging threats. This ongoing assessment helps maintain the effectiveness of DLP and ensures it aligns with your organization’s changing data protection requirements.
Deep Dive into Best Practices for DLP
A deep dive into best practices for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) provides insights into how organizations can design and implement an effective DLP strategy to secure sensitive data, minimize risks, and ensure compliance. Below are key best practices, illustrated with real-world examples, that can help organizations successfully deploy DLP solutions.
Define Clear Data Protection Policies
The foundation of any effective DLP program is the creation of clear and comprehensive data protection policies.
Real-World Example: A healthcare organization implementing DLP to protect patient information might create policies that prevent emails containing PII from being sent to unauthorized recipients or outside the organization. A violation might trigger an alert, and the DLP system could block the transmission of the email, keeping sensitive data safe.
Use a Layered Approach to DLP (Network, Endpoint, and Cloud)
DLP should be applied across multiple layers, network, endpoint, and cloud storage, to ensure comprehensive data protection. A layered approach helps reduce gaps in security, ensuring that data is protected both at rest and in transit.
Real-World Example: A financial institution implements DLP across all three layers to protect customer account details. Network DLP scans outbound emails for sensitive financial data, while endpoint DLP restricts users from transferring data to unauthorized USB devices. In addition, cloud DLP prevents sensitive data from being uploaded to unapproved cloud storage services.
Apply Granular Access Controls
One of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of data breaches is by limiting access to sensitive information. Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) ensures that only those who need access to sensitive data to perform their jobs are allowed to do so.
Real-World Example: In a tech company, developers may only need access to certain code repositories and not sensitive financial data. DLP can enforce these access controls, blocking unauthorized access to customer billing data while allowing developers to work freely within their designated environments.
Monitor and Respond to Data Loss Incidents in Real-Time
Effective monitoring and real-time incident response are essential components of a DLP strategy. Having a system that can detect potential data loss events, such as sending an email with sensitive data to an external recipient, ensures that immediate actions can be taken to mitigate the risk.
Real-World Example: A law firm that handles sensitive legal documents might use DLP to track and prevent the accidental sharing of case files containing client PII. If an employee tries to email a confidential document without encryption, DLP software will either block the email or automatically encrypt it, while alerting the security team.
Integrate DLP with Other Security Solutions
DLP is most effective when it is integrated with other security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), endpoint protection, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Real-World Example: A multinational corporation uses DLP integrated with its SIEM system to monitor user activities across its global network. When an employee from a high-risk region tries to download large amounts of sensitive customer data, the DLP system alerts the security operations center (SOC), which then uses the SIEM platform to correlate this behavior with other suspicious activities, triggering an investigation.
Educate Employees and Promote a Security-Aware Culture
DLP systems are only as effective as the users who operate them. Education and awareness are key in minimizing human errors, such as accidental data leaks or unsafe handling of sensitive information.
Real-World Example: A retail company trains its employees on the importance of securing customer credit card information and the proper ways to share sensitive data within the organization. During onboarding and ongoing training, employees learn how to identify phishing attempts and follow company policies for securely handling customer data.
Regularly Review and Update DLP Policies and Configurations
A DLP strategy should evolve with the organization’s changing needs and the emergence of new threats. Regular reviews of DLP policies and system configurations ensure that they remain effective in protecting sensitive data.
Real-World Example: A healthcare provider might update its DLP policies as new regulations (such as those related to patient data) come into effect. If the provider adopts new technologies like telehealth platforms, it may need to adapt its DLP configurations to protect patient data transferred through these new communication channels.
Successfully implementing DLP requires a multi-faceted approach that includes defining data protection policies, leveraging a layered security strategy, applying granular access controls, monitoring incidents in real time, integrating with other security tools, and educating employees.
A Win-Win Strategy for Data Loss Prevention
A win-win strategy for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on balancing robust security measures with maintaining operational efficiency, fostering a positive user experience, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Rather than seeing DLP solely as a security tool that restricts business processes, a win-win approach involves aligning DLP practices with business goals, ensuring that the protection of sensitive data doesn’t create unnecessary friction or hinder productivity.
Aligning DLP with Business Objectives
For a DLP strategy to be truly successful, it needs to align with the broader goals and operations of the business. This includes understanding the organization’s core values, objectives, and the importance of its data. The goal is not only to prevent data loss but to support the business in its growth and day-to-day activities without excessive overhead.
For example, a company that values innovation and agility should integrate DLP in a way that enables employees to collaborate freely while maintaining security. Instead of restricting access to all external communication channels, the organization might adopt DLP tools that enforce security rules selectively, based on the nature of the data being handled.
Real-World Example: A tech startup that frequently collaborates with external partners could implement a DLP solution that allows sharing of non-sensitive information while encrypting and controlling the transfer of proprietary intellectual property. This approach ensures that business operations continue smoothly, with only the most sensitive data being actively monitored and protected.
Seamless Integration into Daily Operations
For DLP to be successful, it must be integrated seamlessly into daily workflows without creating significant disruption. A win-win strategy means that employees don’t feel their activities are overly scrutinized, which could lead to resistance or inefficiency. Instead, the DLP system should run in the background, automatically protecting data without hindering employees from performing their jobs.
One way to achieve this is by minimizing false positives, incidents where the DLP system flags non-sensitive data or actions as violations. By fine-tuning the DLP rules based on specific organizational needs, businesses can reduce the number of unnecessary alerts, thus ensuring that employees can focus on their tasks rather than dealing with alerts or system restrictions.
Real-World Example: Consider a financial institution that uses DLP to protect customer account details. The DLP system is configured to allow most transactions but will flag and alert security teams only when highly sensitive or specific actions (e.g., transferring large sums of money outside authorized channels) are detected.
User Awareness and Training
Education is a crucial aspect of a win-win strategy for DLP. Employees should be educated about the importance of data security, the role they play in protecting sensitive data, and how the DLP system works. When users understand the purpose behind DLP and the potential consequences of data breaches, they are more likely to follow best practices and feel less burdened by the system.
Training should be practical and tailored. Instead of offering generic security training, organizations should focus on scenarios relevant to employees’ day-to-day responsibilities.
Real-World Example: A healthcare provider can run annual security training programs tailored to each department. Clinical staff might be trained on how to securely handle patient records and avoid mishandling confidential information, while IT professionals receive training on setting up secure systems and responding to security alerts.
Automated and Proactive Protection
A win-win DLP strategy involves automating much of the data protection process, reducing the burden on employees while actively preventing data loss. By automating routine tasks such as encrypting sensitive files or blocking unauthorized access to certain data, organizations can reduce human error and minimize the chances of a data breach.
For example, DLP systems can be set up to automatically encrypt emails that contain sensitive information before they are sent to external recipients.
Real-World Example: A legal firm handling sensitive client documents might configure their DLP software to automatically apply encryption to all files containing confidential client information before those files are emailed or uploaded to the cloud.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops
A successful DLP strategy must include continuous monitoring to track the system’s effectiveness and provide feedback for improvement. By reviewing DLP performance regularly and assessing its impact on both security and business operations, organizations can adjust policies and rules to better balance protection and productivity.
Monitoring is not just about detecting violations but also about understanding trends in employee behavior, types of incidents, and emerging threats. By integrating DLP data with other security tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, businesses can have a more holistic view of their security posture.
Real-World Example: A multinational corporation with a global workforce uses DLP to track data transfers and monitor employee activities. By analyzing the data collected from the DLP system, the company identifies certain employees in high-risk regions who are transferring unusually large amounts of data.
Regulatory Compliance with Flexibility
Many organizations need to comply with industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, which dictate how sensitive data should be handled. A win-win DLP strategy ensures compliance while providing the flexibility to continue conducting business smoothly. DLP systems should be able to meet the specific regulatory requirements for data protection, while also allowing the organization to adapt its practices as regulations evolve or as business needs change.
Rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach, DLP solutions can be tailored to meet the specific compliance requirements of different regions or industries.
Real-World Example: A cloud service provider that handles client data from various industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, and retail) may need to comply with different regulations in each sector. By implementing a flexible DLP solution that allows the provider to configure rules based on industry-specific compliance needs, the company can securely store and transfer data without compromising on compliance or productivity.
Clarifying Terms Related to Data Loss Prevention
Clarifying terms related to Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is essential for understanding how DLP works and its role in protecting sensitive data across organizations. DLP encompasses a range of concepts, technologies, and policies, all designed to prevent the unauthorized access, sharing, or loss of critical data.
- Sensitive Data: Sensitive data refers to any information that must be protected from unauthorized access due to its confidentiality, integrity, or legal importance.
- Data Loss: Data loss occurs when sensitive information is unintentionally exposed, transferred, or deleted without authorization.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Data Loss Prevention refers to the set of technologies, policies, and practices used to monitor, detect, and prevent the unauthorized transfer, sharing, or leakage of sensitive data outside an organization’s network.
- DLP Policies: DLP policies are the set of rules that define how sensitive data should be handled, stored, transmitted, and shared within an organization.
- Endpoint DLP: Endpoint DLP refers to the protection of sensitive data on end-user devices, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices.
- Network DLP: Network DLP monitors data as it moves across an organization’s network, preventing unauthorized data transfers or communications.
- Cloud DLP: Cloud DLP focuses on securing sensitive data that is stored or shared in cloud environments.
- Data Classification: Data classification is the process of categorizing data based on its level of sensitivity and importance.
- Policy Violation: A policy violation occurs when a user or system activity goes against the defined DLP policies.
- Alerting and Reporting: Alerting refers to the notifications that are triggered when a DLP policy violation is detected.
- Content Inspection: Content inspection is a core component of DLP, where the system analyzes the actual content of files, emails, or communications for sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, or personal health data.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption is the process of converting data into a secure format that cannot be read without the appropriate decryption key. In the context of DLP, encryption ensures that even if sensitive data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable.
- Insider Threat: An insider threat is a security risk that originates from within the organization, often from employees or contractors who have access to sensitive data and systems.
- Zero Trust Security Model: The Zero Trust security model operates on the principle that no user or device, whether inside or outside the corporate network, should be trusted by default.
General FAQ for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software
What is Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software and why is it important?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software is a security solution designed to monitor and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, leakage, or theft. It helps prevent accidental or intentional data breaches by controlling how data is accessed, shared, or transferred across an organization’s network. The importance of DLP lies in its ability to secure sensitive information, such as personal, financial, or intellectual property data, thereby safeguarding privacy, ensuring regulatory compliance, and protecting an organization’s reputation.
How does DLP software detect sensitive data?
DLP software typically uses content inspection and contextual analysis to identify sensitive data. It scans files, emails, and network traffic for specific patterns, keywords, and data types that match predefined rules, such as credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, or personally identifiable information (PII). Machine learning and data fingerprinting techniques may also be employed to improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives.
What types of data does DLP software protect?
DLP software protects various types of sensitive information, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial data (e.g., credit card information), healthcare records (e.g., under HIPAA), intellectual property (e.g., patents, trade secrets), and other confidential business data (e.g., contracts, legal documents). The software can be configured to detect and block the transfer of such data across different channels.
Can DLP software prevent all types of data breaches?
While DLP software is a critical tool for preventing unauthorized access and data leakage, it cannot guarantee the prevention of all breaches. It is highly effective in controlling data access and transfers, but it may not fully protect against sophisticated attacks, insider threats, or human error. Organizations should deploy DLP as part of a broader cybersecurity strategy that includes access controls, encryption, employee training, and other preventative measures.
How does DLP software handle cloud environments and SaaS applications?
DLP software is increasingly designed to protect data in cloud environments and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications. It can monitor and control data uploaded to cloud storage services (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox), or shared within cloud-based applications (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft 365). Cloud DLP can enforce policies such as encrypting sensitive data before upload or preventing the sharing of sensitive documents with external parties.
Can DLP software impact employee productivity?
If not configured properly, DLP software can impact productivity by blocking legitimate actions or generating unnecessary alerts. However, modern DLP solutions are designed to minimize disruptions by allowing organizations to fine-tune policies, reduce false positives, and offer exceptions where appropriate. Educating employees about data security and the importance of DLP can also help foster understanding and cooperation, reducing resistance to security measures.
How does DLP software integrate with other security solutions?
DLP software often integrates with other cybersecurity tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, firewalls, encryption software, and endpoint protection. These integrations allow organizations to have a more comprehensive view of their security posture, streamline incident response, and provide a unified approach to managing threats across multiple layers of the IT infrastructure.
What is the role of encryption in DLP software?
Encryption is often a key component of DLP solutions. When a DLP policy violation is detected, encryption can be applied to sensitive data to ensure it is unreadable if intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals. DLP software may automatically encrypt data before it is transmitted or stored, protecting sensitive information while allowing authorized users to continue accessing and sharing the data securely.
How does DLP software detect and respond to insider threats?
DLP software is designed to detect and mitigate both malicious and accidental insider threats by monitoring employee behavior and data access patterns. It can detect activities such as unauthorized attempts to copy, move, or share sensitive data, and take actions like blocking the transfer, alerting security teams, or applying encryption. By setting up policies based on user roles, DLP can ensure that employees only have access to the data they need for their job, minimizing the risk of insider threats.
Is DLP software scalable for large organizations?
Yes, DLP software is highly scalable and can be tailored to meet the needs of both small businesses and large enterprises. For large organizations with diverse data environments, DLP solutions offer centralized management dashboards, automated policy enforcement, and integration with other enterprise security tools.
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of DLP software?
Organizations can measure the effectiveness of DLP software by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as the number of policy violations detected, the number of incidents prevented, the number of false positives, and response times to security alerts. Regular audits, user feedback, and periodic reviews of policies and system performance can help id
Does DLP software require constant updates and monitoring?
Yes, DLP software requires ongoing monitoring and updates to remain effective. As new threats and vulnerabilities emerge, DLP solutions should be updated to handle them.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software is an essential part of any modern organization’s cybersecurity strategy, providing robust protection for sensitive data against both external threats and insider risks.