Third-Party Applications Management Software is a type of software solution used to oversee, manage, and control third-party applications that are integrated into an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Discover the top 7 third-party patch applications management software solutions
Patchmypc
Patchmypc – Manual patching wastes time, risks errors, and leaves systems vulnerable. Automate updates with secure, efficient solutions for ConfigMgr, Intune, and WSUS.
- Real-time tracking of new software releases
- Our team tests and delivers updates within 24 hours of release
- Each update undergoes rigorous testing to ensure compatibility and reduce deployment risks
- Patch My PC provides detailed vulnerability (CVE) information, helping IT teams prioritize critical patches
- We handle the complexities of vendor installers, streamlining the packaging process for you
- Patch My PC offers robust customization options to tailor updates and deployment workflows to your specific needs
- Our team, including Microsoft MVPs, has deep expertise in ConfigMgr and Intune, supporting millions of endpoints worldwide
Recastsoftware
Recastsoftware – Manage and patch all third-party applications in your organization from one centralized location with the largest application catalog on the market!
- Automated Updates are within Reach
- Comprehensive Coverage: Patch Management to Application Management
- Centralized Application Management
- Automate Security Updates with Confidence
Ivanti
Ivanti – Proven, industry-leading patch management to keep all your systems and third-party apps up to date and compliant.
- Deploy thoroughly tested patches to thousands of machines within minutes, with minimal network disruption
- Simplify patch management across multiple operating systems
- Secure your most vulnerable applications, such as Acrobat Flash, Java, and various Internet browsers
- Patch all devices, whether they’re behind firewalls, on the go, at remote locations, or even in sleep mode
- Optimize ROI and minimize risks associated with third-party applications
- Patch virtual machines, offline systems, and hypervisors seamlessly
- Manage software updates from a unified interface
- Effortlessly ensure enterprise-wide patch compliance to meet organizational policies and regulatory requirements
Scalefusion
Scalefusion – Automate 3rd party application patching on Windows & Mac devices with agent-based management. Enhance security and efficiency with effortless patch updates.
- Keep your third-party apps up-to-date and minimize exposure to threats
- Improve your device and app performance, stability, and speed
- Meet compliance standards. Avoid penalties. Stay confident
Action1
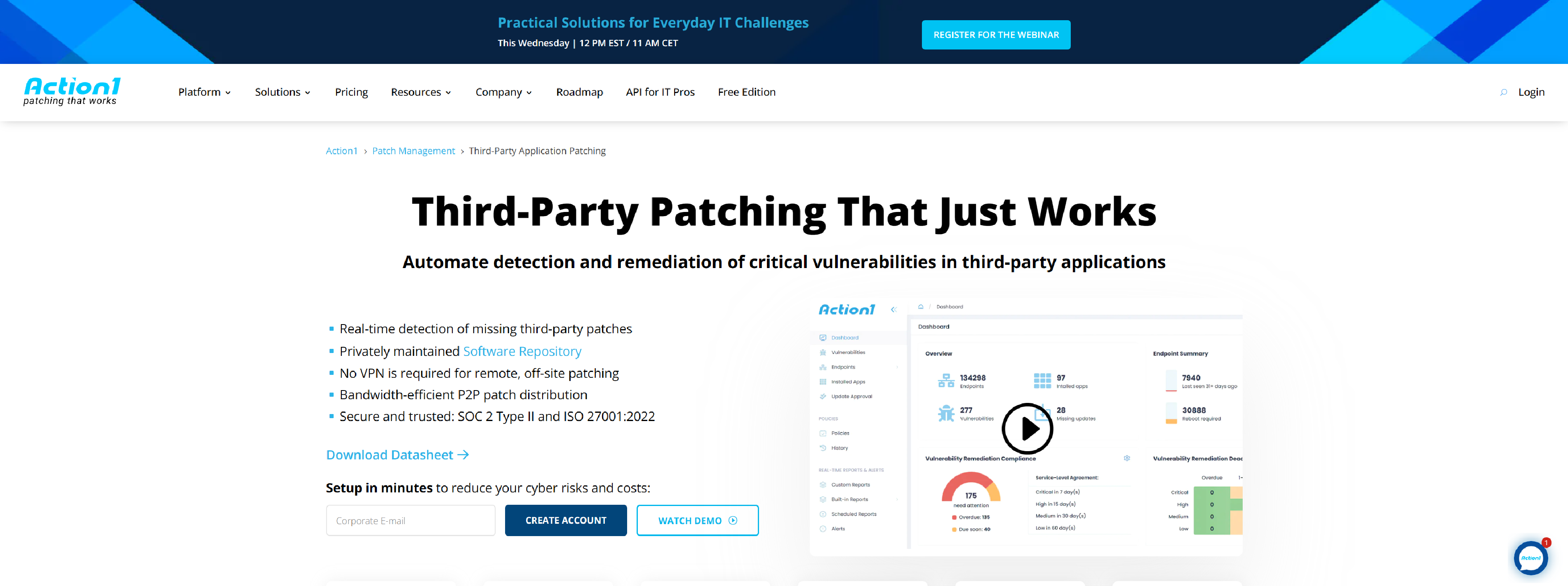
Action1 – Automate detection and remediation of critical vulnerabilities in third-party applications.
- Unlike many community-driven software repositories, the Action1 Software Repository is securely managed by a dedicated, in-house team of trained Action1 patch management specialists
- Accelerate patch delivery and reduce bandwidth strain, all without the need for local appliances or cache servers
- Quickly identify missing third-party patches in real time, eliminating the reliance on outdated scan results from previous days
- Customize your patching schedule and set automated criteria based on severity, update type, vendor, or specific applications
- Flexible reboot options allow users to save their work and delay restarts for a limited time, while still enforcing patching deadlines
- Action1 is the only third-party patch management solution certified with both SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001:2022 standards
N-able
N‑able’s RMM platforms provide third-party patch management for over 100 applications.
- More applications, more surface area to secure
- The more common the application, the more vulnerable
- Centralized third-party patching
- Control and reduce third-party applications to optimize patches
42gears
SureMDM third-party app catalog can streamline mobile application management on Windows devices.
- Eliminate the need for manual downloads and redeployments when updating apps
- IT administrators can easily access over 4,500 applications from a unified repository
- Choose whether apps install automatically (immediately or on a scheduled basis) or allow users to select updates from the SureMDM App Store
- Manage third-party apps with a straightforward three-step process: search for an app, add it, and configure update settings
Why Do You Need a Third-Party Applications Management Tool?
A Third-Party Applications Management Tool is essential for several reasons, particularly for organizations that rely on external software for their daily operations.
Centralized Management
- Streamlined Oversight: It allows IT teams to manage all third-party applications from a single platform, saving time and reducing complexity.
License Compliance and Cost Control
- Ensure Compliance: Managing licenses and staying compliant with vendor terms is critical to avoid legal risks. A management tool helps track license usage, renewals, and expirations to ensure that the organization stays within legal boundaries.
- Cost Efficiency: By monitoring application usage and license allocations, organizations can avoid over-purchasing or underutilizing software, which can help reduce unnecessary expenses.
Security and Risk Management
- Address Vulnerabilities: Third-party applications can introduce security risks if not properly managed. A management tool helps to monitor for vulnerabilities, apply patches, and ensure that the software meets the organization’s security standards.
- Reduce Cybersecurity Threats: Managing third-party applications helps to mitigate risks associated with outdated software, which could be exploited by cybercriminals.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Improve Performance: By monitoring the performance of third-party software, organizations can ensure that it runs efficiently, minimizing downtime or disruptions in business operations.
- Identify Underperforming Software: A management tool can help identify underperforming or redundant applications that can be replaced or eliminated to improve overall efficiency.
Update and Patch Management
- Automated Updates: Third-party applications frequently release updates or patches to fix bugs, improve features, or enhance security. A management tool can automate this process, ensuring that updates are applied consistently across all devices.
- Reduce Risk of Obsolescence: Regular updates ensure that applications remain compatible with evolving IT infrastructures and do not become obsolete or unsupported.
Integration and Compatibility
- Seamless Integration: Third-party applications often need to integrate with internal systems or other external applications.
- Avoid Compatibility Issues: Without proper oversight, third-party applications might conflict with existing software.
User Support and Troubleshooting
- Simplified Troubleshooting: A management tool can help track issues with third-party software, enabling IT teams to troubleshoot more efficiently and resolve problems faster.
- Access to Vendor Support: Many management tools offer built-in support ticketing or integration with the vendor’s support system, making it easier to escalate and resolve issues related to third-party software.
Scalability
- Adapt to Growth: As an organization grows and adds more software tools, managing a diverse set of third-party applications manually becomes impractical.
Data Integrity and Backup
- Backup and Restore: Some third-party applications may require data backups or offer sensitive data management.
Vendor Relationship Management
- Track Vendor Performance: The tool can also help organizations manage their relationships with third-party vendors, tracking service levels, contract terms, and performance metrics to ensure they are getting value for money.
Key Features of Third-Party Applications Management Solutions
Third-Party Applications Management Solutions help organizations efficiently manage, monitor, and secure the external software or applications they use.
- Centralized Application Inventory Management: Provides a centralized repository of all third-party applications used within an organization, including details like version numbers, licensing information, and installation status.
Example: Flexera Software helps organizations maintain a comprehensive inventory of all third-party software, making it easier to track installed applications, their versions, and licenses.
- Automated Software Deployment and Updates: Automatically deploys and updates third-party applications across multiple devices or systems, ensuring consistency and minimizing manual intervention.
Example: ManageEngine Desktop Central allows for automated deployment and patching of third-party applications across endpoints, ensuring that they are always up to date and compliant with the latest security standards.
- License and Compliance Management: Tracks third-party software licenses to ensure compliance with vendor agreements, preventing over-deployment or unauthorized use. It also manages renewals and ensures the organization isn’t exposed to legal or financial risks due to non-compliance.
Example: ServiceNow Software Asset Management offers robust license management to help organizations track software usage and compliance with licensing terms for third-party applications.
- Patch and Vulnerability Management: Automates the process of applying patches to third-party applications to address vulnerabilities, ensuring that software remains secure and free from known exploits.
Example: Ivanti Patch Management supports third-party application patching and vulnerability scanning, helping organizations ensure their applications are secure by automating patch deployment.
- Security and Risk Assessment: Assesses the security posture of third-party applications and identifies potential risks, such as vulnerabilities, outdated versions, or misconfigurations.
Example: Tenable integrates with application management solutions to perform risk assessments, identifying vulnerabilities in third-party applications and providing actionable insights to mitigate those risks.
- Integration with Existing IT Ecosystem: Ensures seamless integration with other internal systems, like IT Service Management (ITSM), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), or vulnerability management tools, to streamline workflows and improve operational efficiency.
Example: BMC Helix ITSM integrates with third-party application management tools, enabling businesses to automate ticketing, patching, and compliance workflows directly from the ITSM interface.
- Software Performance Monitoring and Analytics: Continuously monitors the performance of third-party applications, providing insights into how the applications are performing and helping to identify issues that may impact user experience or productivity.
Example: Datadog offers performance monitoring for third-party applications, tracking metrics like response time, uptime, and resource consumption to ensure optimal performance.
- Automated End-of-Life (EOL) Tracking: Tracks the end-of-life dates for third-party applications, ensuring that outdated and unsupported software is either updated or replaced before it poses security or compliance risks.
Example: SolarWinds Patch Manager tracks the lifecycle of third-party software, notifying administrators when an application is nearing its EOL so they can take appropriate action.
- Vendor Management and Support Integration: Provides tools for managing relationships with third-party software vendors, including tracking support requests, service level agreements (SLAs), and updates.
Example: Cherwell ITSM allows businesses to manage vendor relationships, track support tickets, and integrate vendor-specific information with the application management solution.
- User Access and Permissions Control: Manages user access to third-party applications, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access, based on role-based access controls (RBAC) or other authentication mechanisms.
Example: Okta provides identity and access management (IAM) capabilities to ensure that only authorized users can access specific third-party applications, integrating with your broader security framework.
- Audit and Reporting: Generates detailed reports on the usage, security, compliance status, and patching history of third-party applications. This helps organizations demonstrate compliance with internal policies or external regulations.
Example: Snow Software provides audit and reporting capabilities that track software usage, compliance status, and licensing across all third-party applications in an organization.
- Integration with Asset Management: Integrates with asset management systems to track physical and virtual hardware that supports third-party applications. This helps ensure that software deployment and asset usage are aligned.
Example: Cherwell Asset Management integrates with third-party applications, tracking the devices and environments where applications are deployed, and ensuring effective asset management.
- Cloud and On-Premises Support: Supports both cloud-based and on-premises third-party applications, enabling management of a hybrid environment where some applications are cloud-hosted, while others are installed locally.
Example: Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) helps organizations manage third-party applications across both cloud and on-premises environments, providing flexibility in hybrid deployment scenarios.
- Change Management and Version Control: Tracks changes in third-party applications, including version updates and configuration changes, ensuring that changes are properly managed, tested, and rolled out in a controlled manner.
Example: Jira Service Management allows organizations to manage the lifecycle of changes to third-party applications, integrating seamlessly with change management processes and workflows.
- End User Support and Helpdesk Integration: Provides integrated helpdesk or support ticketing features for end users encountering issues with third-party applications.
Example: Zendesk integrates with third-party applications to provide a unified support ticketing system, enabling users to report issues with applications and receive timely resolutions.
Best Practices for Using Third-Party Applications Management Software
To effectively use Third-Party Applications Management Software, it’s important to centralize the management of all third-party software, ensuring proper tracking and updates. Automating deployment and patch management helps maintain security and compliance. Regularly monitor application performance and security, testing updates before full deployment to avoid disruptions. Keep track of licenses to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. Fostering good vendor relationships, providing user training, and regularly reviewing software for redundancy will help optimize usage and efficiency.
FAQs About Third-Party Applications Management Software
What is Third-Party Applications Management Software?
Third-Party Applications Management Software is a tool designed to help organizations manage, monitor, and secure the external software applications they use. It assists with tasks like deployment, updates, license management, security patching, and performance monitoring of applications that are not developed in-house but are critical for business operations.
Why is Third-Party Applications Management important?
Managing third-party applications effectively is essential for ensuring security, compliance, and operational efficiency. These applications often introduce security vulnerabilities, licensing risks, and performance issues. Proper management ensures that software is up-to-date, secure, and compliant with relevant standards or regulations, minimizing potential risks and optimizing business performance.
How does Third-Party Applications Management Software improve security?
By automating patch management and vulnerability assessments, Third-Party Applications Management Software helps ensure that third-party applications remain secure by applying necessary security patches quickly.
Can this software help with license compliance?
Yes, these solutions track licenses for third-party applications, ensuring the organization does not exceed license limits or miss renewal deadlines.
How does it help with performance monitoring?
Third-Party Applications Management Software often includes features for monitoring the performance of external software. This includes tracking application usage, response times, and resource consumption.
Is it suitable for both cloud and on-premises applications?
Yes, many Third-Party Applications Management tools are designed to manage both cloud-based and on-premises software.
What happens if a patch causes issues with an application?
Most management software includes features for testing patches before full deployment, and if an issue arises, rollback options are available to restore the previous stable version.
How do I integrate Third-Party Applications Management Software with other systems?
Many Third-Party Applications Management tools can integrate with existing IT management systems, such as IT Service Management (ITSM), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), or asset management platforms.
How do I ensure smooth vendor management with this software?
The software can help track vendor contracts, performance, and updates, facilitating a proactive approach to managing third-party relationships. By keeping track of support tickets, renewals, and SLAs, organizations can ensure that they are getting the most value from their third-party software vendors.
How do I manage multiple third-party applications efficiently?
Centralizing management through Third-Party Applications Management Software provides a unified dashboard to monitor and control all third-party applications from a single location.
With the right solution, organizations can streamline operations, maintain control over their IT environment, and ensure that all third-party applications contribute to business productivity and security.