The term “Change Control” is one of the latest buzzwords in the IT industry. However, the term need not be restricted to the IT industry alone. The world has always been susceptible to change; however, the need for managing changes smoothly is felt the most nowadays across industries, especially the IT industry. This article will discuss about change control and its impact.
Change control relates to the procedures that are needed to introduce changes in IT products and services in a controlled manner. Addressing ad hoc changes needs to be coordinated well. Change control is a major component of a much broader subject – Change Management.
The change control process ensures that a product, service or a process is only modified according to the requirements of a change that is necessary. It has been observed in the IT industry that ad hoc, unnecessary changes have introduced bugs in software applications. People learn from experiences and a formal change control management activity was introduced in the software product life cycle.
A change “freeze point” was defined and all changes after that were discarded until the software was released in the initial phase. Some changes have risks and/or considerable financial implications. Some changes in this category are – operating system upgrades, change in network routing tables, and even something very basic to business – a change in contractual terms. Needless to say, this kind of changes need to be addressed through an organized, well-coordinated change control process, if possible with the aid of change control software (for example advanced Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools).
- A formal change control process comprises of the following steps:
- Record/Classification of changes
- Assessment of change impact
- Planning of change management
- Build/Test the modification areas
- Formal Implementation of changed product/service
- Closure of the change issue and obtaining acceptance from the client
At the very beginning, there is a “change initiation” from the client side. A person then has to record the change request and categorize it. The classification has to be done on the merits of the change, say “major”, “minor”, and “normal”. Thereafter, the change has to be prioritized as “emergency”, “to be expedited”, and “routine”.
Next, a thorough impact analysis has to be done. Impact assessors typically convey their risk analysis by answering a set of questions both to the concerned business and IT heads. Based on this analysis, the manpower planning for the change implementation is carried out. This change implementation unit is formally called the Service Delivery Unit (SDU). The analysis should be carried out from two corners – business justification, and technical justification.
The SDU team takes up a major role in the change control management activity. The very first thing that an SDU carries out is to plan the change implementation. A regression plan has also to be in place. Their plan has to be agreed upon by the core change control source committee, sometimes formally known as Change Advisory Board (CAB). If the plan is approved, modifications are made according to plan within the boundaries of a planned date. The product/application then has to be tested thoroughly with a compulsory regression-testing phase. After the change is implemented, the CAB should conduct a post implementation review.
Lastly, the client has to observe the effects of the change and give sign-off to the development party.
Let us now discuss about the goals of change management. First, most companies want that changes should have minimal impact on existing day-to-day functions. They want to ensure that affected users should be well trained about the change control process and existing documentation (like user manual/online help) should be modified suitably. Secondly, no company wants to recall existing software that has been running well because of mishandling of changes. There should be electronic tracking of changes suitable for auditing purposes. Positive impact of the change should be detectable and measurable as much as possible. Lastly, all companies want optimal and economic utilization of all resources involved in the change implementation. Change implementation causes lot of effort and money. All’s well that ends well. Every company will naturally be happy if all the time and money bears fruit at the end.
After the process and goals, let us discuss finally about the individual people contributing to the change control management activity and their respective roles. Change Initiator is the person who initiates the change request and confirms the completion of change implementation. Change Sponsor is the person who gives business approval to the change. Change Administrator is the person who carries out the initial investigation and conducts change assessment. This person also monitors change requests. Impact Assessors are people who analyze the likely impact of the change. The Change Manager is in charge of the entire managerial activity related to the change implementation. This person has lots of authoritative power and acts as a single point of contact and mediator among non-agreeing parties. Finally, the Task Owners are the people who are in charge of implementing specific tasks that add up to the actual change implementation.
Software Change Management For Better Performance
The only thing constant in life perhaps is change. The Information Technology industry, the backbone of today’s business world, is no exception either. New technological innovations, data capturing techniques, system analysis, coding practices, and software enhancements are governed by change – constant, palpable, and at times subtle. In this article, we will explore the nature of software change management and the attributes of a change management system.
In today’s globalized world, the business environment has become too complex, particularly in case of geographically distributed entities. Today’s high capacity distributed systems can handle high volume sensitive business data, and have to cater to activity requests of varied types. This complex scenario has necessitated the practice of software change management, a new practice under the broader discipline of software project management.
A change management system allows software development companies to streamline software process in order to respond to change requirements more proactively. The practice prompts adherence to standardized methods and procedures in order to minimize the impact on other relevant areas of the software. The aim is to keep the overall system stable without touching a majority of the modules. Time and effort need to be factored in also. Every valid change request must be promptly addressed with minimum efforts.
Software process management needs to be robust enough to tackle external demands ranging from legislative impositions to initiatives in customer service enhancements. Another beneficial effect of change management system is that it strives to maintain a proper balance between the need to implement changes, and the negative effect of changes in a stable system. After all, we need to understand at some point of time that “change is not necessarily a progress”. Each phase of software development life cycle – IT project and portfolio management; requirement capture and feasibility study; requirement analysis; application design; coding; testing and debugging; user acceptance and overall lifecycle quality management – need to be practiced keeping provisions of the inevitable change requirements. The result of such a system is high visibility and greater predictability of software applications with respect to changes.
One or more of the following components may get affected due to the impact of changes:
- Hardware
- System software
- Communication equipments
- Application software
- All related documentation like design documents, user manuals etc.
Scope and Extent of Software Change Management
The first and foremost requirement of a change management system is the implementation of defined (and documented) steps to handle change requirements. Once established, the practice should spread to all areas of the software process management system. Today’s IT houses have already established change-handling mechanisms. At the beginning, software engineers and analysts pay attention to individual changes. However, in today’s business environment, organizations function in geographically distributed areas catering to diverse client segments. Naturally, an enterprise system cannot function like discrete information silos. An impact of a change in a particular segment of the software often has little to moderate effect in other segments also. If the overall system impact is not taken into account, inefficiencies may creep into the system. Such inaccuracies, if not addressed early, may lead to devastating impact at a later stage.
According to a research, about 45% of software development companies cater to software development initiatives that spread across geographical boundaries and cultures. The extent of change requests handled by these companies can easily be imagined. Over the years, the software engineering discipline has stressed the importance of measurements and metrication in handling changes. The mandatory internal and external audits have enforced process management practices. All these activities have a huge contribution towards software change management.
According to industry analysts, the competency in change management as achieved by software companies in general leaves much to be desired. The challenge is not only from the geographical distribution aspect. Organizational activities like mergers and acquisitions, inability to cope up with rapid hardware and software innovations and monetary concerns in times of economic recession contributes largely towards inefficiencies in change management.
A collaborative approach across functional silos is crucial in achieving a successful change implementation. All processes, including automation mechanisms must work in tandem in order to attain the broader goal of application stability in spite of continual change tremors.
Let us summarize the known building blocks of a well-coordinated change management system below:
- All development practices should be driven by well-defined processes
- Every activity in the software development life cycle should be properly controlled and measured
- An efficient asset management practice should be in place. This will help in optimum usage of assets
- There should be proper time management for all activities
- Change requirements must be properly validated in order to filter out the most pressing ones with respect to business criticality, time, money, and resource availability aspects
- A proper communication chain should exist in order to communicate change requests promptly across geographically distributed teams
- An efficient change tracking mechanism should be in place
- Geographically distributed teams should work in a scalable, expandable, and secure technical infrastructure
- Support from all quarters need to be garnered
GIVAINC
Founded in 1999, Giva was among the first to provide a suite of help desk and customer service/call center applications architected for the cloud.
- Simple and intuitive approach to Standalone Change Management
- Interactive RFC monthly calendar provides an overview of the entire change management process
- Easy to use change request and approval workflows
- Hardware & software assets can be linked to change requests
- All details and files are included in one place
- Giva works based on your workflow and the way you work
- Weekly view of RFC calendar assures that changes do not conflict
- Robust, fast & painless compliance reporting for higher quality decision-making
SOLARWINDS
SolarWinds IT monitoring and management tools are built for SysAdmins and network engineers who need powerful and affordable tools. Get a free trial today.
- To help you prepare well in advance and define your plans
- To improve IT services alignment towards business plans and goals
- To enhance risk assessment capabilities
- To reduce the impact of the change in day-to-day business activities
- To improve employee productivity and service quality
SUNVIEWSOFTWARE
SunView Software is a leading provider of IT Service Management (ITSM), Change Management & Service Desk solutions powered by award-winning artificial intelligence & machine learning.
- Faster Change Processing
- Better Visibility Into All Changes
- Compliance Reporting Has Never Been Easier
- Get Change Management Connected
- Optimized Change Processes For Each Team
SYSAID

SysAid is an IT service management solution that offers all the ITIL essentials. It’s everything you need for easy and efficient ITSM in a single tool.
- Responding to changing business requirements while maximizing value and reducing incidents, business disruption, and re-work
- Responding to the business and IT requests for change that will better align IT services with business needs
- Ensuring that all changes are recorded and evaluated, and that authorized changes are prioritized, planned, tested, implemented, documented, and reviewed in a controlled manner
- Ensuring that all changes to configuration items are recorded in the configuration management database (CMDB)
- Optimizing, and reducing where possible, the overall business risk
UPBOARD
upBOARD: Team collaboration & enterprise software with free online business best practices tools & templates for project management, business strategy, change management, innovation processes, & metrics dashboards.
With upBOARD, you get an entire end-to-end process with proven tools, templates, and metrics dashboards for organizational change management, instantly and designed by the experts.
RALLEO
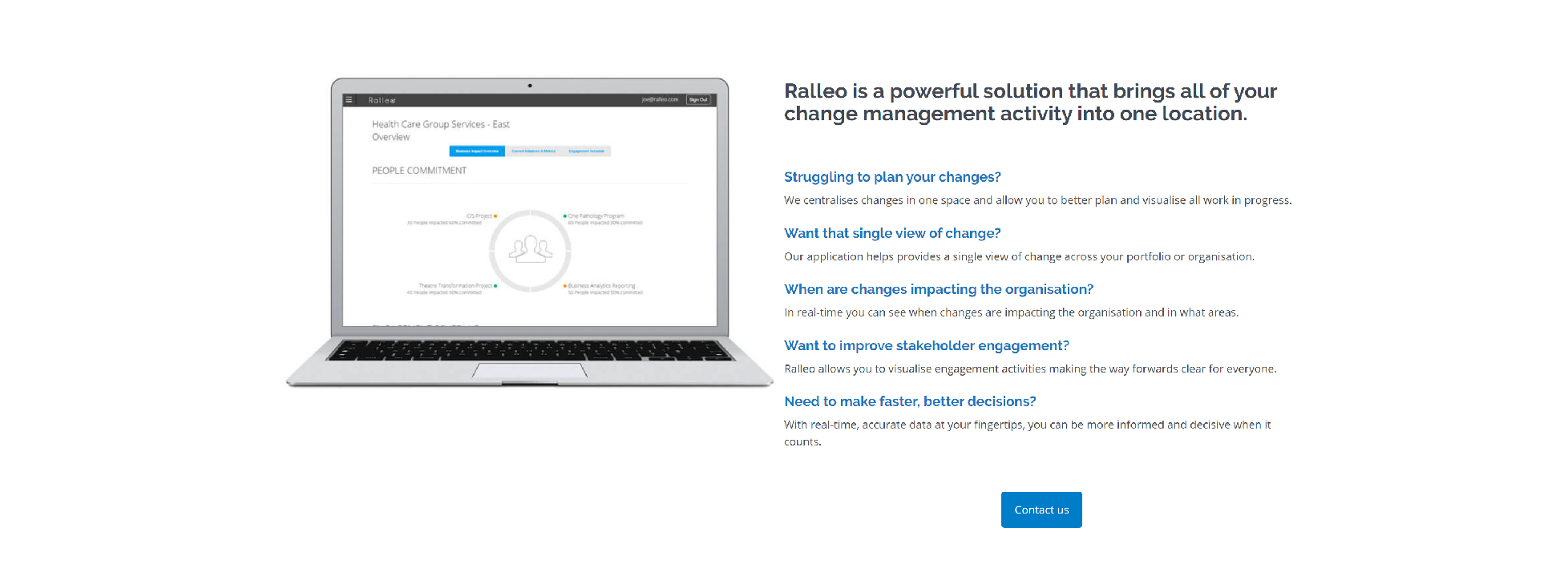
Instead of trying to manage change with Microsoft Excel spread sheets, have everything you need in one place.
- Provides a single view of change
- Supports any change methodology
- Better change planning
- Manage business impacts
- Improves business engagement
- Provides real-time metrics
- Increases visibility and accessibility of change
- Focus on what matters
- Drives a consistent approach
- Improves the effectiveness of your change team
- Improves resource utilisation
- Simplifies integrations
- Ensures data security and reliability
AGILOFT
Agile business software: Agiloft is the world’s most adaptable and rapidly deployed enterprise software for Contract Management, Service Desk and Custom Workflows.
- Database Schema
- Configurable Tables and Forms
- Configurable Data Fields
- Field Types
- Drag and Drop Layouts
- Multi-Tab Input Forms
- Collapsible Form Sections
- Choice Lists
- Relationship Diagrams
- Table Relationships
- Power User Dashboards
- Easy Access Left Pane
- Data Views
- Edit Multiple Records
- Quick Edit
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- and More.
INTELLECT
Intellect’s New Cloud BPM Software Platform allows you to automate complex business processes easily with no-coding, drag and drop app development capabilities.
- Improve transparency with automation, version control, and workflows in the change management process.
- Submit change requests and control plan revisions at any point in the production process and track all revisions
- Empower employees with access to change requests, process flow alterations and updated process and design changes
- Real-time notifications and validations for approvals, change executions and implementations
ARENASOLUTIONS
Arena engineering change management software is an essential part of your product realization success.
- Automates the review process with criteria-based routing, deadlines, and notifications
- Tracks changes throughout the product lifecycle and provides in-context linking to the affected product record and related processes
- Ensures complete change package with critical information like inventory disposition codes
THECHANGECOMPASS

The Change Compass is a digital cloud-based change capacity planning tool. Get Change management software tools and change impact analysis tools to manage strategic portfolio for the companies improve customers experience.
- Dashboard
- Employee heat map
- Business Unit Analysis
ROCKETSOFTWARE
Rocket helps companies worldwide optimize and modernize their IBM Z, IBM Power, and MultiValue platforms to help create new user experiences and efficiencies.
- Change request management
- Workflow and change management
- Software configuration management
- Distribution and release management
ENABLON
Enablon solutions help companies manage environmental and social performance, ensure compliance, minimize risks and improve profitability by leveraging some of the world’s most advanced technologies.
- Streamline and Standardize Change Management
- Enhance Efficiency of Change Management
- Identify and Mitigate Operational Risks
- Improve Operational Efficiency
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance
MYBLUELABEL
MyBlueLabel offers a SaaS (Software as a Service) which focuses on simplifying Project Portfolio- and Quality Management for companies of all sizes.
- Root Cause Analysis
- End-To-End Tracking
- Realistic Timeline